by Gelogia Team | Jul 7, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
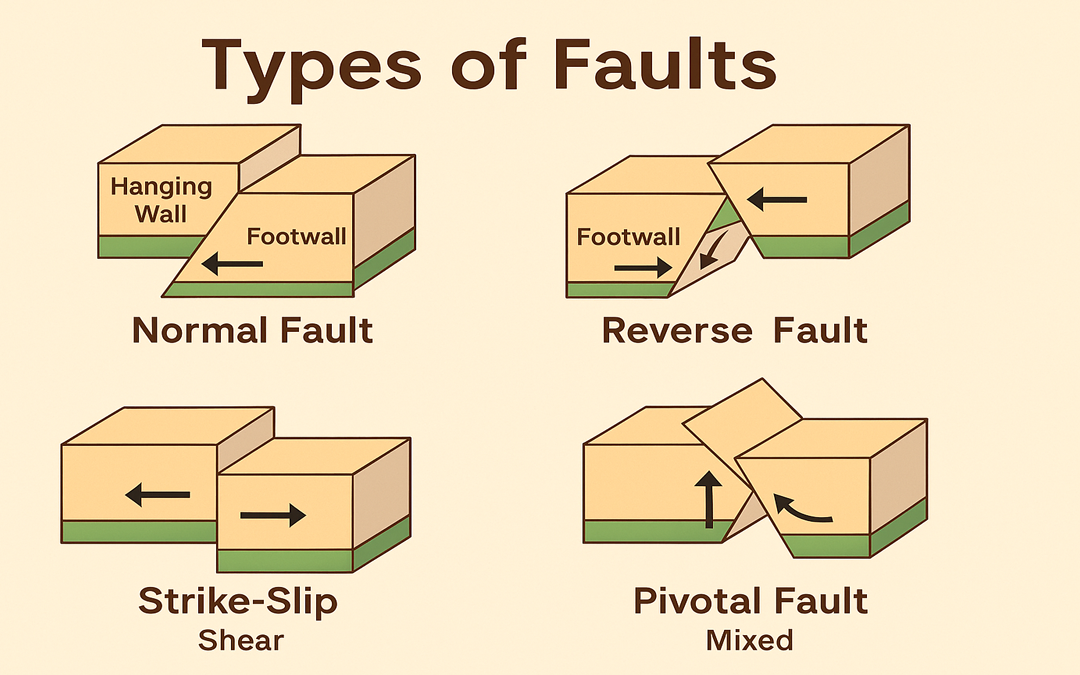
Faults are fractures in the Earth’s crust where blocks of rock have moved past each other due to tectonic forces. These movements are caused by stresses such as compression, tension, and shearing. Understanding the types of faults is essential in geology to interpret...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 6, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
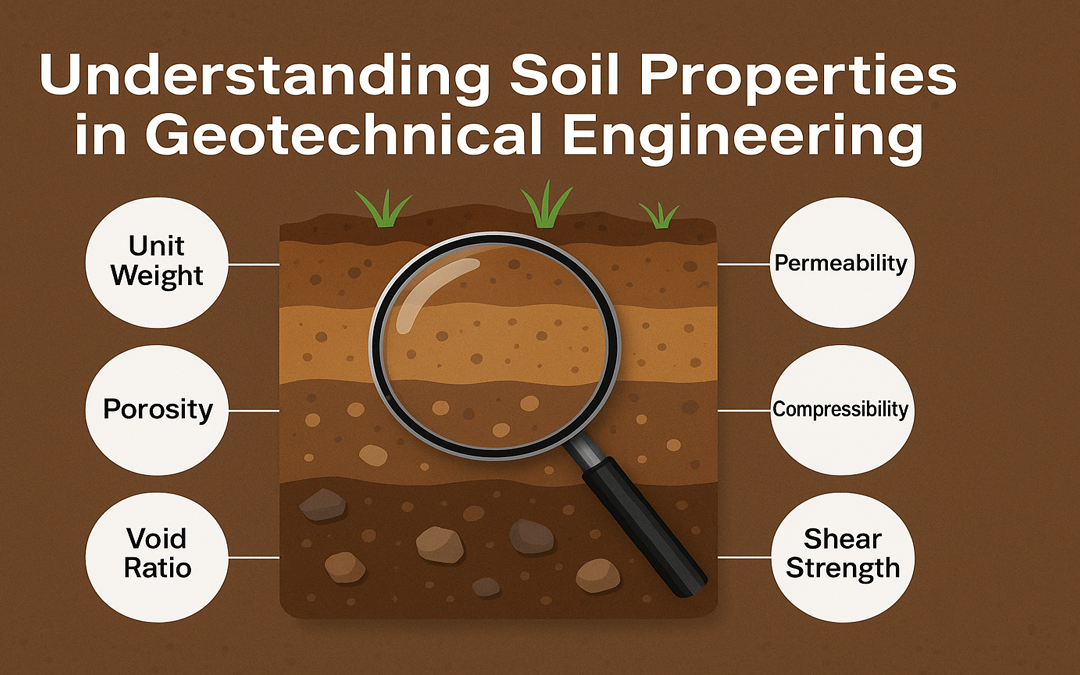
Soil properties are fundamental characteristics that define how soil behaves under various conditions. In geotechnical engineering, understanding these properties is essential for analyzing ground stability, designing foundations, and ensuring safe construction...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 28, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
Soil forms the foundation of agriculture, construction, and ecosystems. Farmers, engineers, and environmentalists must understand the types of soils to make informed decisions. This guide explores the classification of soils based on grain size, origin, composition,...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 27, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
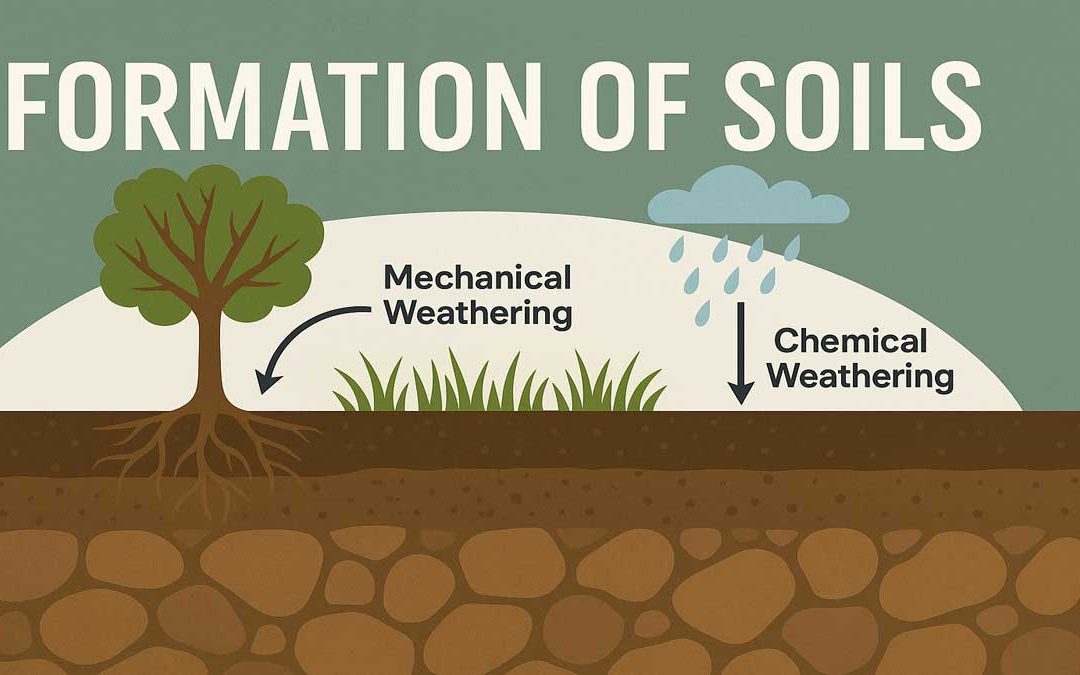
The formation of soils begins as a natural geological process that breaks down rocks into finer particles. Weathering — both mechanical and chemical — gradually turns solid rock into loose, fertile soil that supports plant life. Formation of Soils: Soil refers to a...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 22, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
The Mercalli Intensity Scale provides a way to measure earthquakes not by scientific instruments alone, but by the effects felt by people and damage observed in the built environment. Unlike magnitude scales (which measure energy released), the Mercalli scale ranks an...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 21, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
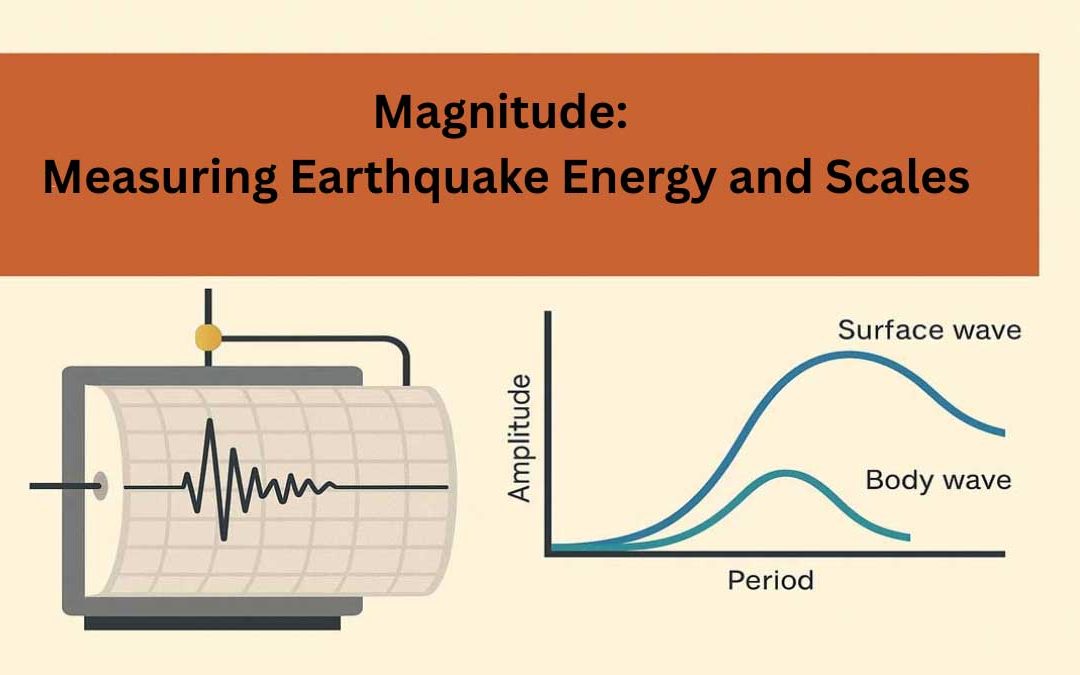
Magnitude is a measurement of the energy released by an earthquake. Earthquake magnitude scales in general do not directly represent any physical parameters of the source. Magnitude scales can be used to represent the relative size of earthquakes. Why Are Magnitude...