by Gelogia Team | Jun 28, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
Soil forms the foundation of agriculture, construction, and ecosystems. Farmers, engineers, and environmentalists must understand the types of soils to make informed decisions. This guide explores the classification of soils based on grain size, origin, composition,...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 27, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
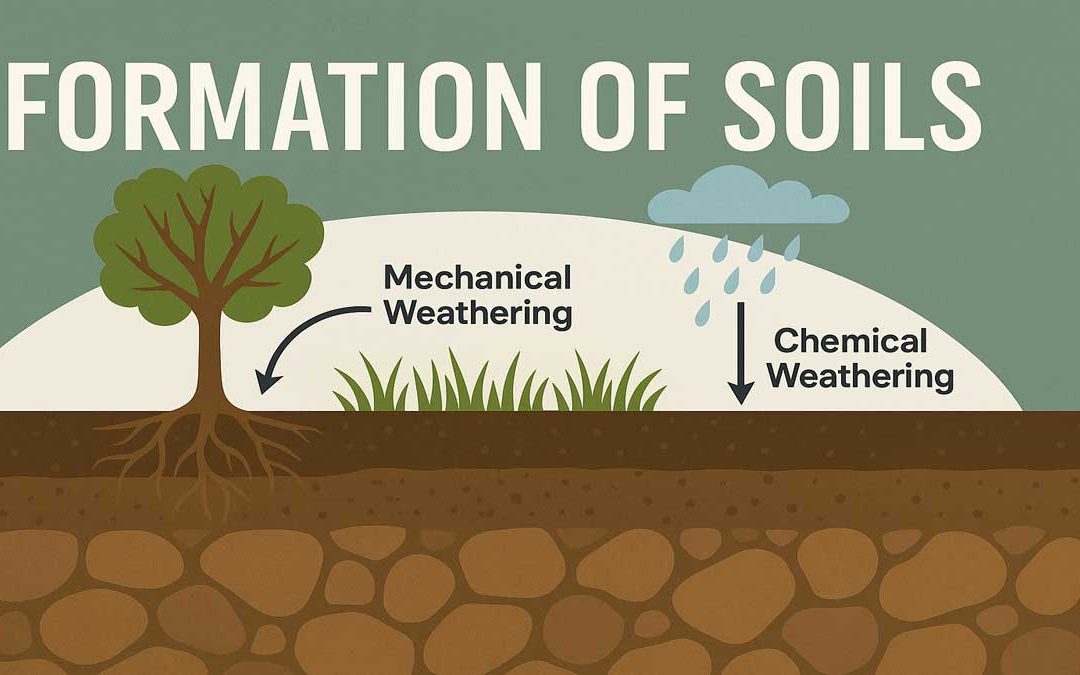
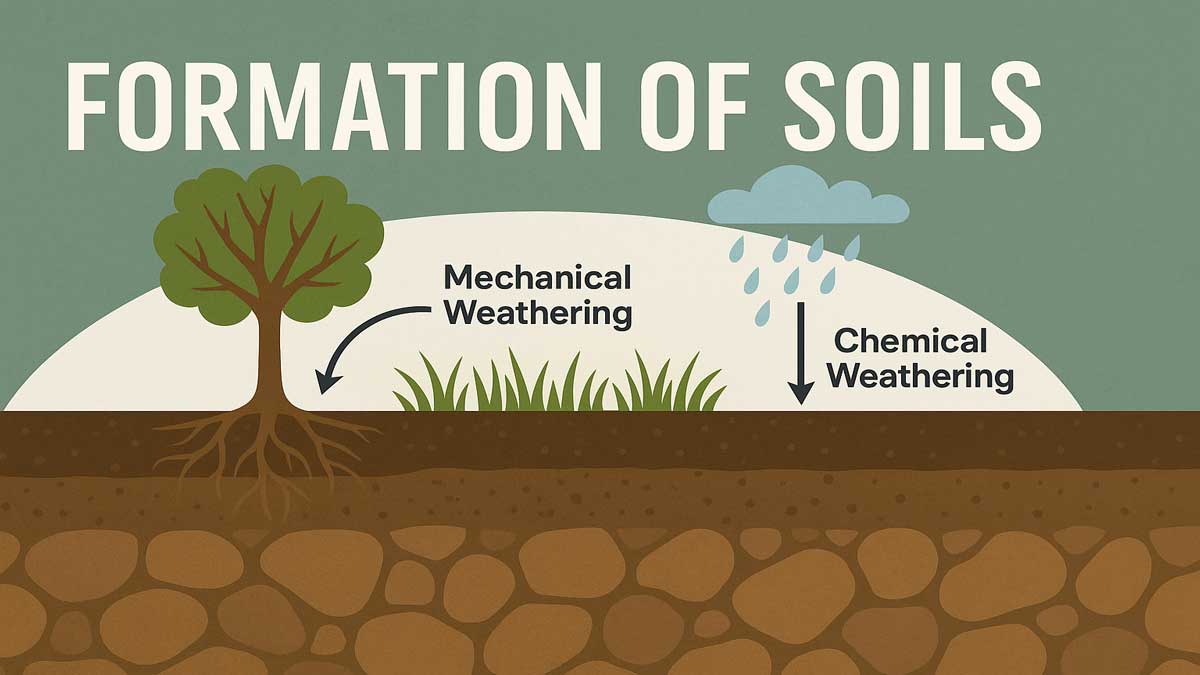
The formation of soils begins as a natural geological process that breaks down rocks into finer particles. Weathering — both mechanical and chemical — gradually turns solid rock into loose, fertile soil that supports plant life. Formation of Soils: Soil refers to a...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 22, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
The Mercalli Intensity Scale provides a way to measure earthquakes not by scientific instruments alone, but by the effects felt by people and damage observed in the built environment. Unlike magnitude scales (which measure energy released), the Mercalli scale ranks an...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 21, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
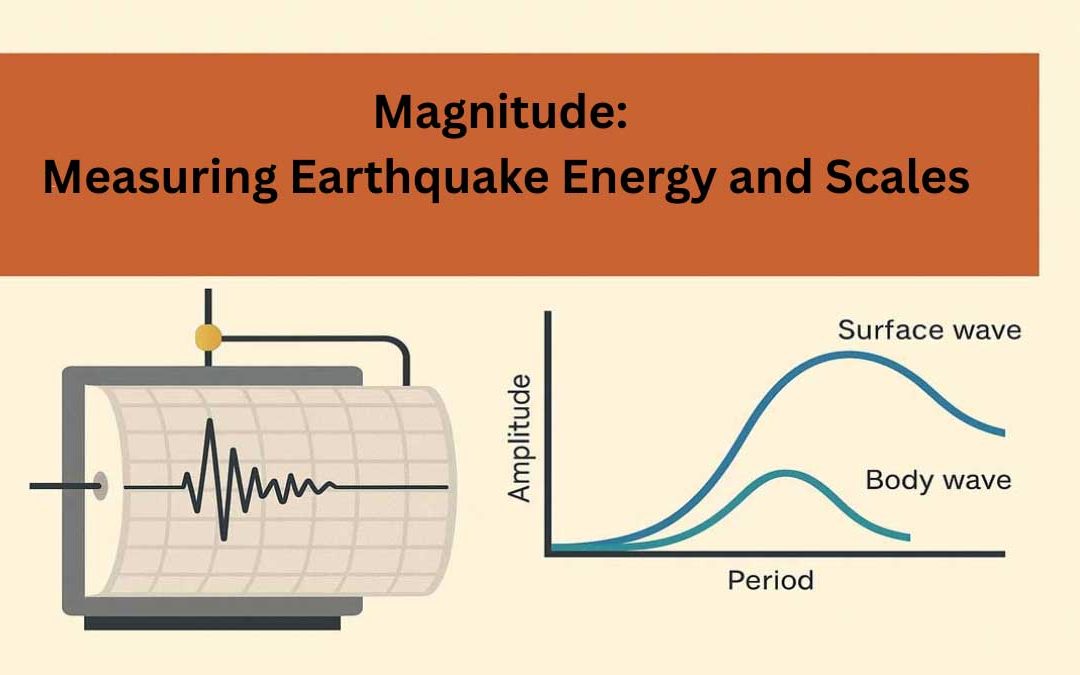
Magnitude is a measurement of the energy released by an earthquake. Earthquake magnitude scales in general do not directly represent any physical parameters of the source. Magnitude scales can be used to represent the relative size of earthquakes. Why Are Magnitude...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 20, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
A seismograph is an essential device used by scientists to measure and record earthquakes. By understanding how seismographs work, we can better interpret seismic activity and improve earthquake preparedness. How Does a Seismograph Work? A seismograph is the device...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 19, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
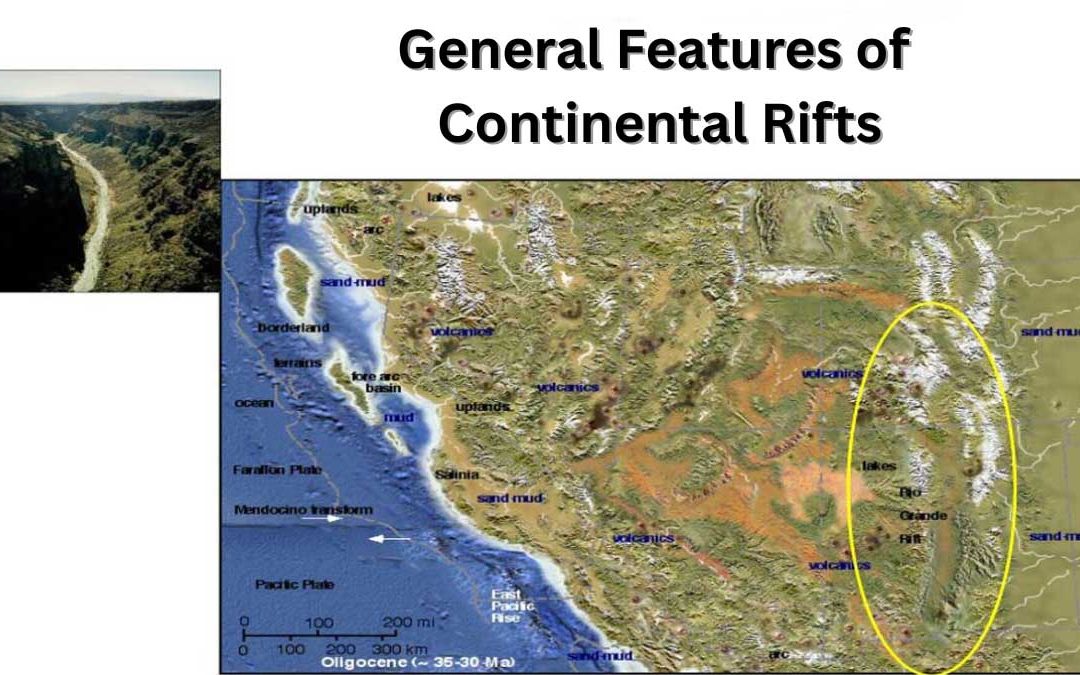
Continental rifts are geological zones where the Earth’s crust is stretched and broken, forming deep fault-bounded valleys. These structures play a key role in understanding plate tectonics, continental breakup, and the formation of new ocean basins. This...