by Gelogia | Nov 4, 2024 | Mineralogy
Chemical Equilibrium: When the rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal, the concentration of the reactants and products remains constant. This stage is called chemical equilibrium. Characteristics of Chemical Equilibrium: Constancy of concentration Can...

by Gelogia | Nov 1, 2024 | Mineralogy
Thermodynamics focuses on the interactions between heat, work, and temperature, exploring how these elements connect to energy, entropy, and the physical characteristics of matter and radiation. These interactions are defined by three fundamental laws of...

by Gelogia | Oct 30, 2024 | Mineralogy, Structural Geology
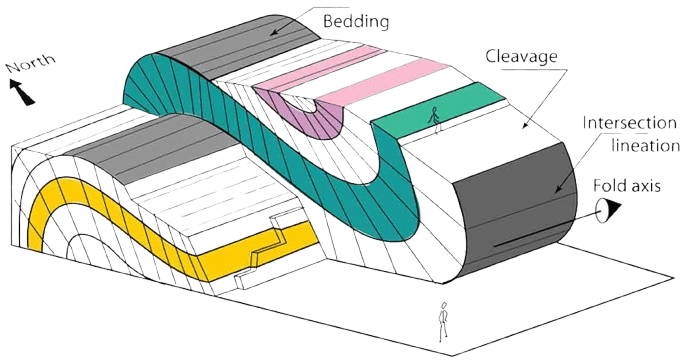
Lineation: Lineation is expressed by the parallelism of some directional property in the rock. Types of lineation: Lineation is found to develop in igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Lineation is of two types: primary lineation (sedimentary rocks, igneous...

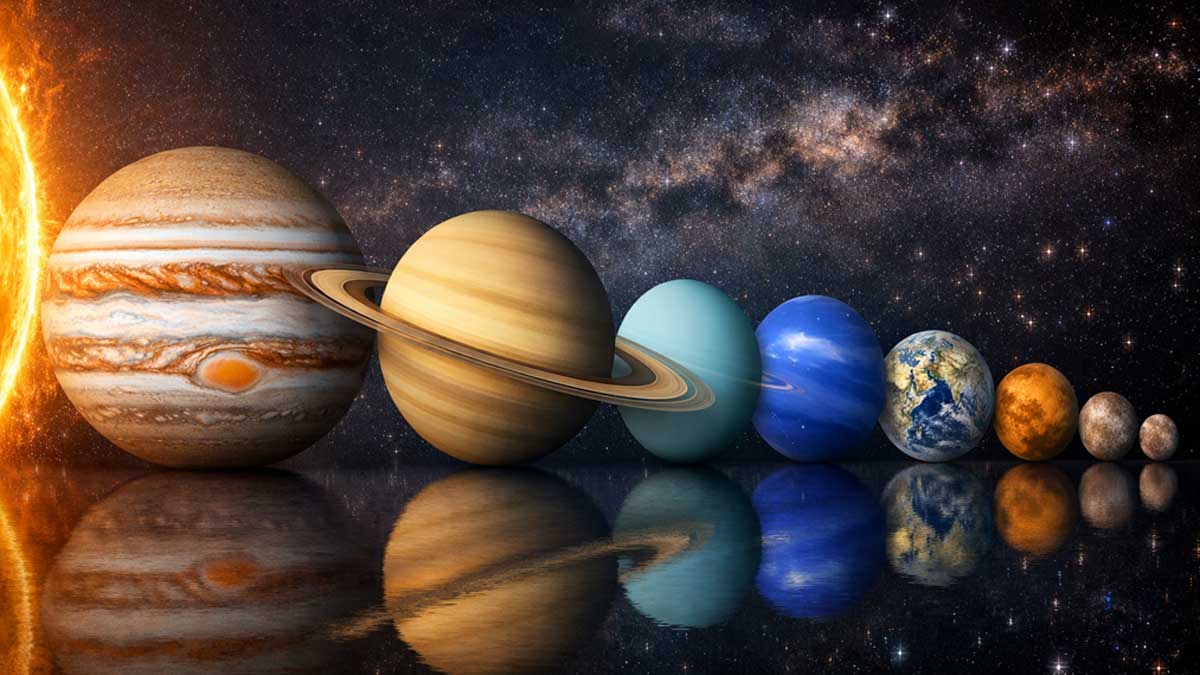
by Gelogia | Oct 28, 2024 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Uncategorized
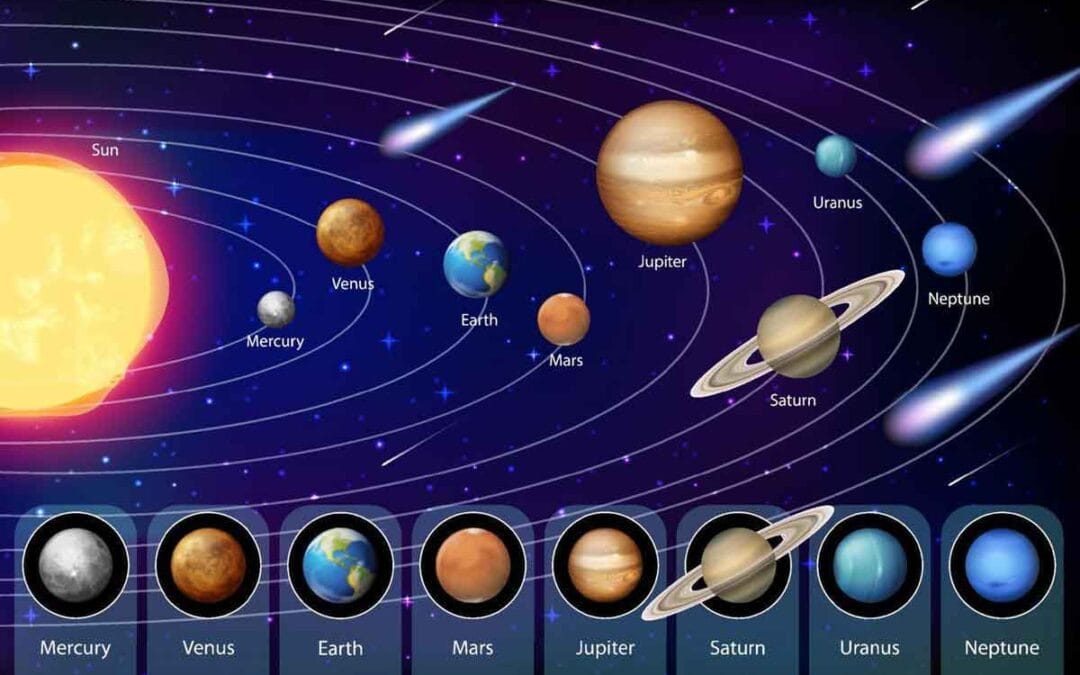
The solar system consists of the Sun and all celestial objects that orbit around it under the force of gravity. Scientists believe the solar system formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of gas and dust collapsed, creating the Sun and a surrounding...

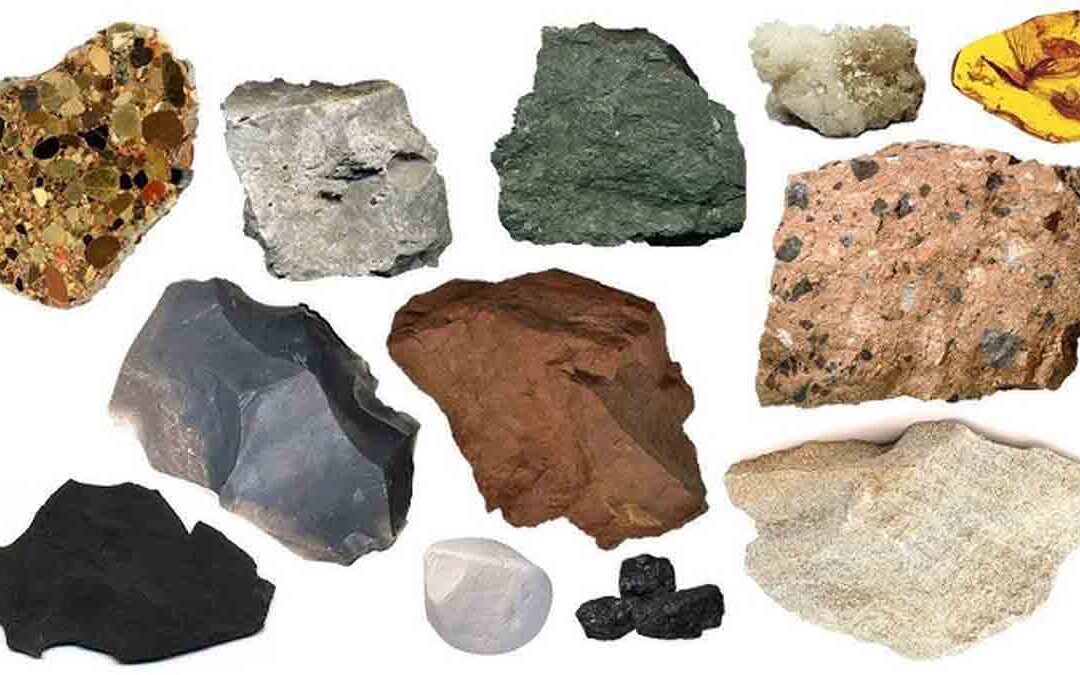
by Gelogia | Oct 27, 2024 | Petrology
Sediments are materials formed due to mechanical or chemical activity by the agents of denudation on preexisting rocks. They are deposited in a stratified fashion, layer after layer, at the surface of the lithosphere. Lithification of the sediments at relatively low...