by Gelogia Team | Jul 1, 2025 | Crystallography & Mineral Optics, Mineralogy
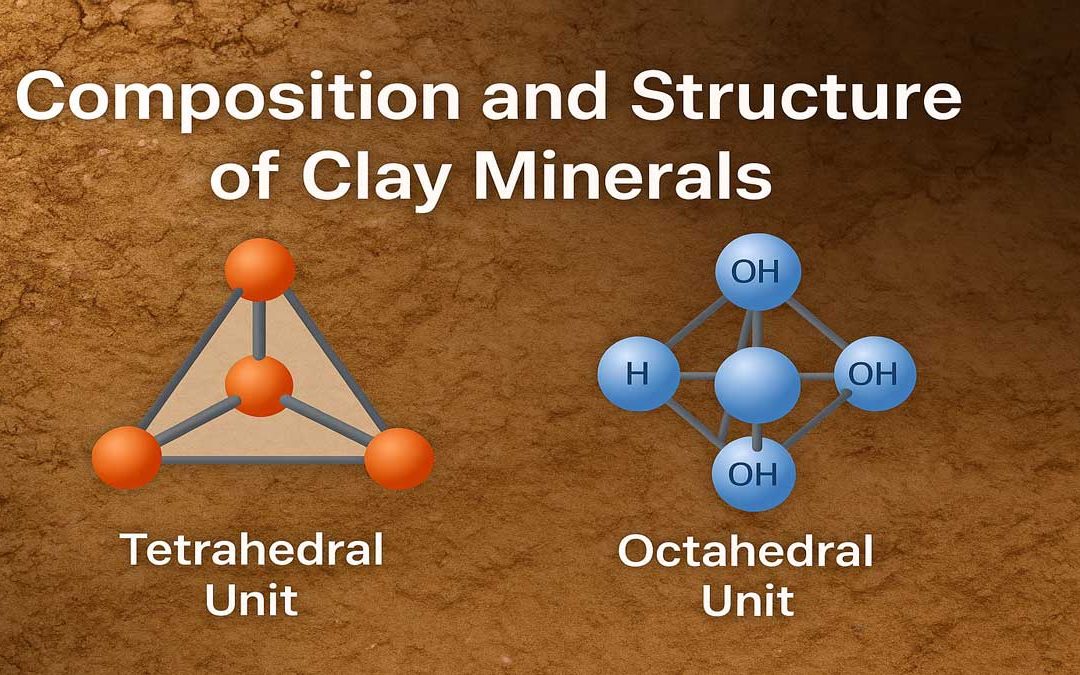
Clay minerals are microscopic, layered silicate minerals that form the fine fraction of soils and sediments. They consist mainly of hydrous aluminum silicates and often include magnesium, iron, and organic materials. Their unique structure made up of tetrahedral and...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 28, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
Soil forms the foundation of agriculture, construction, and ecosystems. Farmers, engineers, and environmentalists must understand the types of soils to make informed decisions. This guide explores the classification of soils based on grain size, origin, composition,...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 27, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
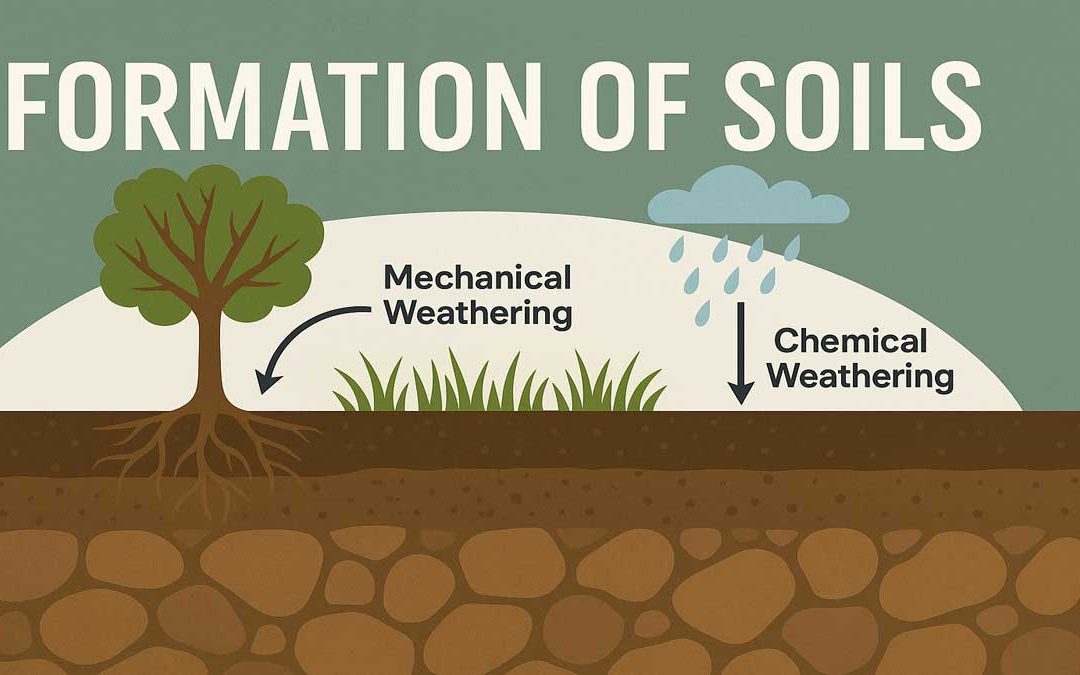
The formation of soils begins as a natural geological process that breaks down rocks into finer particles. Weathering — both mechanical and chemical — gradually turns solid rock into loose, fertile soil that supports plant life. Formation of Soils: Soil refers to a...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 25, 2025 | Uncategorized
Engineering Geology is the study of how geology is used in engineering work. It helps engineers understand rocks, soil, and water before building roads, bridges, dams, tunnels, and other structures. This blog explains what Engineering Geology is, its history, why it...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 22, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
The Mercalli Intensity Scale provides a way to measure earthquakes not by scientific instruments alone, but by the effects felt by people and damage observed in the built environment. Unlike magnitude scales (which measure energy released), the Mercalli scale ranks an...