by Gelogia Team | Jul 24, 2025 | Mineralogy
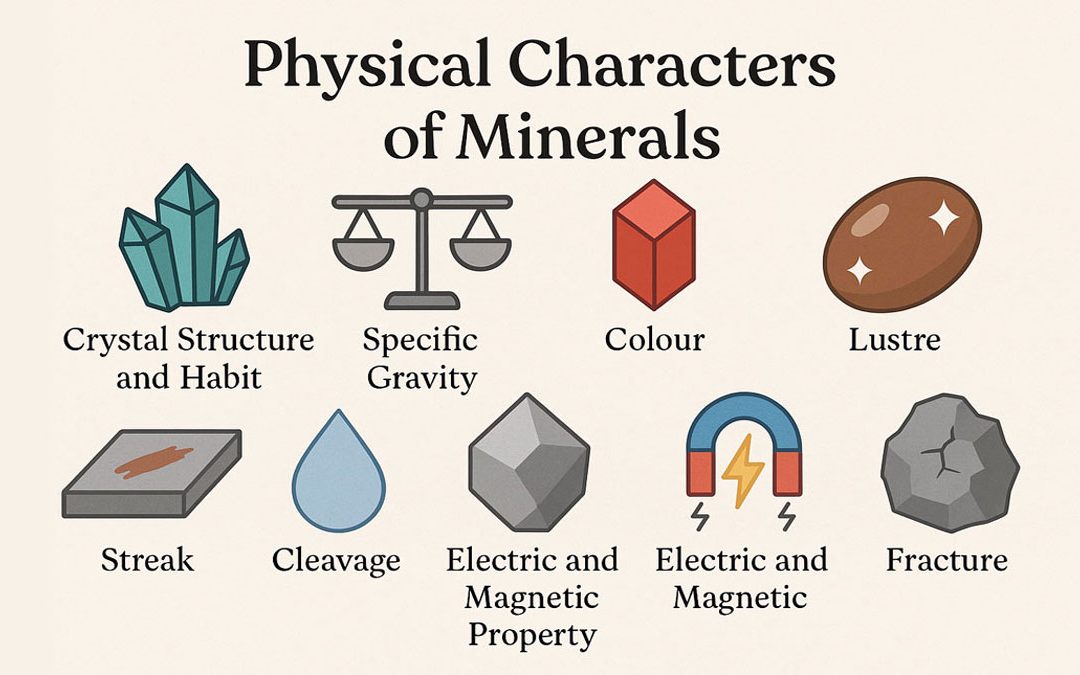
The physical characteristics of minerals are essential traits used to identify and classify them accurately. These characters offer insights into a mineral’s behavior, structure, and properties under various conditions. Below is a detailed breakdown of the important...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 21, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Stratigraphy, Structural Geology
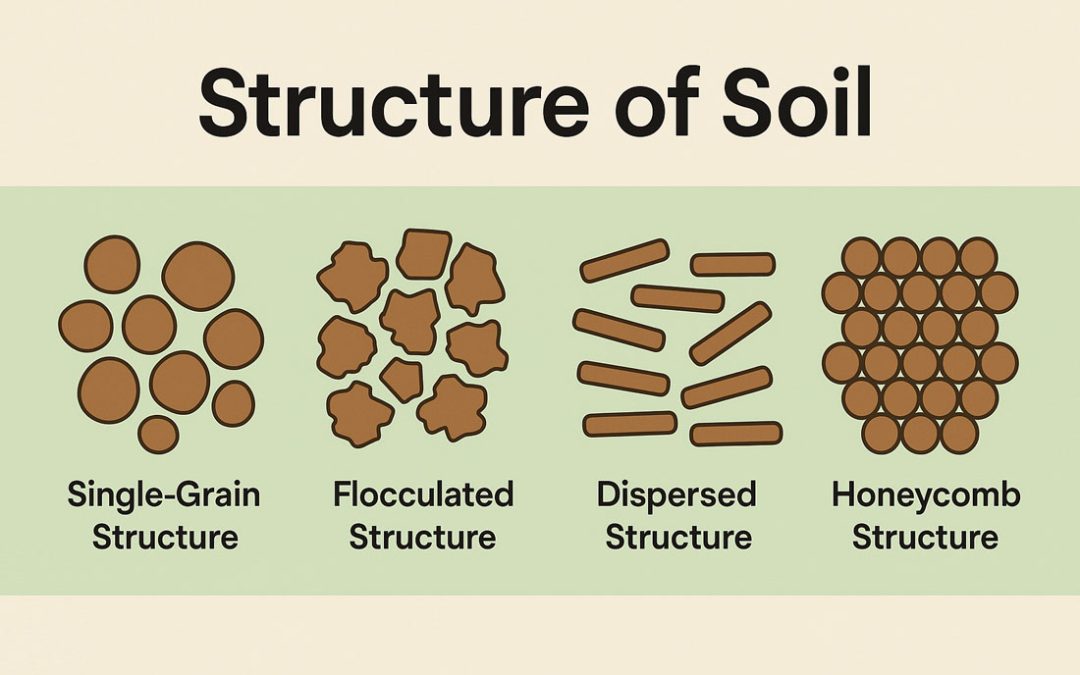
Soil structure refers to how soil particles arrange themselves within the matrix, which includes voids, fissures, and cracks. Several factors influence soil structure, such as the shape and size of particles, mineral composition, grain orientation, interactions...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 20, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
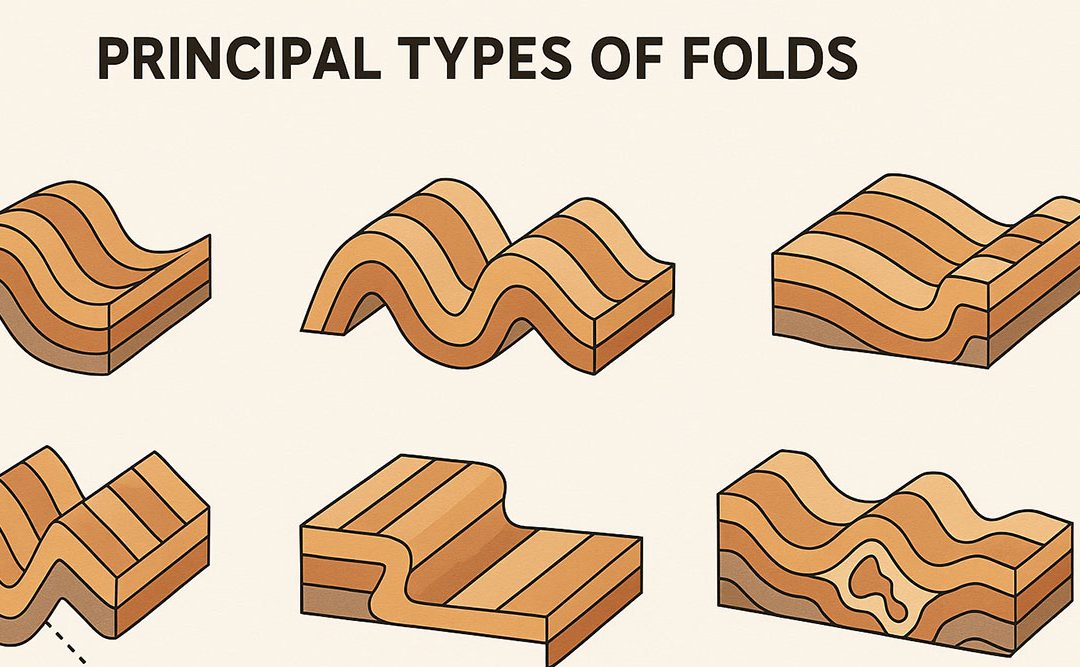
Folds are significant geological structures formed when rock layers undergo compression, resulting in bending without fracturing. They are commonly observed in deformed sedimentary, metamorphic, and even igneous rocks. Understanding the different types of folds and...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 19, 2025 | Structural Geology
Types of Bridges: There are five major types of bridges, namely Girder or Beam Bridge, Cantilever Bridge, Arch Bridge, Suspension Bridge, and Cable-Stayed Bridge. The magnitude of the load of the bridge and the forces acting on the support system considered in the...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 19, 2025 | Historical Geology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology
James Hutton, usually described as the “Father of Modern Geology,” plays a critical role in the field of Earth sciences. His innovative insights contested prevailing perspectives on the Earth’s history and established the basis for contemporary...