The density of soil refers to the mass of soil within a given volume. It helps us understand how compact or loose the soil is, which is important for construction, farming, and soil testing. Different types of soil density, like bulk density, dry density, saturated density, and submerged density, are measured based on the soil’s moisture and condition. Knowing soil density helps engineers build strong structures and farmers improve soil health.
Density of Soil:
The density of a soil is defined as the mass of the soil per unit volume. Density may be of different types, such as bulk density, dry density, saturated density, and submerged density.
Determination of density requires measurement of the weights and volumes of the soil sample in the laboratory in different states, such as dry, saturated, or submerged conditions, depending upon the type of density to be determined. In the metric system, density is expressed in g/cm³. For calculation purposes, the unit weight of water is taken as 1 g/cm3.
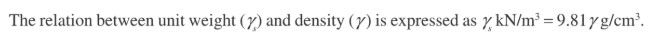
Types of Soil Density:
Soil density can vary depending on moisture content and the condition of the soil. The main types include Bulk density, Dry density, Saturated density, and Submerged density. Each type represents the soil’s mass per unit volume under specific conditions and is used for different engineering or agricultural purposes.




Conclusion:
In simple terms, the density of soil tells us how tightly soil particles are packed together. By understanding the different types of density, we can make better decisions in building projects, land development, and agriculture. Whether it’s for checking compaction or ensuring soil strength, soil density plays an important role in many real-world applications.






