by Gelogia Team | Jun 25, 2025 | Uncategorized
Engineering Geology is the study of how geology is used in engineering work. It helps engineers understand rocks, soil, and water before building roads, bridges, dams, tunnels, and other structures. This blog explains what Engineering Geology is, its history, why it...

by Gelogia Team | Apr 7, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Uncategorized
Resistivity: This is a fundamental physical property of metal in a wire. Though related to resistance, it is not the same. Resistance (R) depends on length, area, and the material’s properties, which are collectively described by this term.R = ρL/A, where:R =...

by Gelogia Team | Mar 29, 2025 | Structural Geology, Uncategorized
Geothermal energy, a renewable energy source, comes from the Earth’s internal heat and results from geological processes like subsidence in sedimentary basins. As sedimentary layers bury, temperature and time increase, driving the thermal maturation of organic...

by Gelogia Team | Mar 15, 2025 | Structural Geology, Uncategorized
Capillary pressure: Capillarity is the phenomenon whereby liquid is drawn up a capillary tube. It is a measurement of the force that draws a liquid up a thin tube, or capillary. It increases with decreasing tube diameter. Translated into geological terms, the...

by Gelogia Team | Mar 14, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Uncategorized
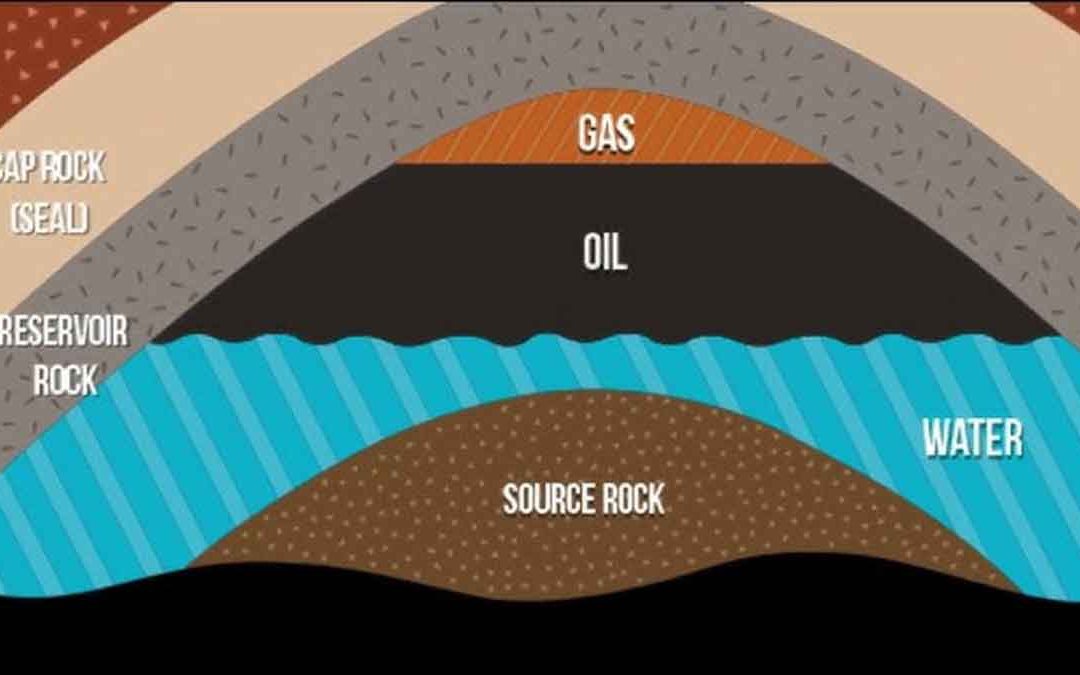
Source Rocks: A Petroleum source rock is defined as any rock that has the capability to generate and expel enough HC to form an accumulation of oil or gas. A potential source rock is one that is too immature to generate petroleum but will form significant quantities...

by Gelogia Team | Mar 13, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Uncategorized
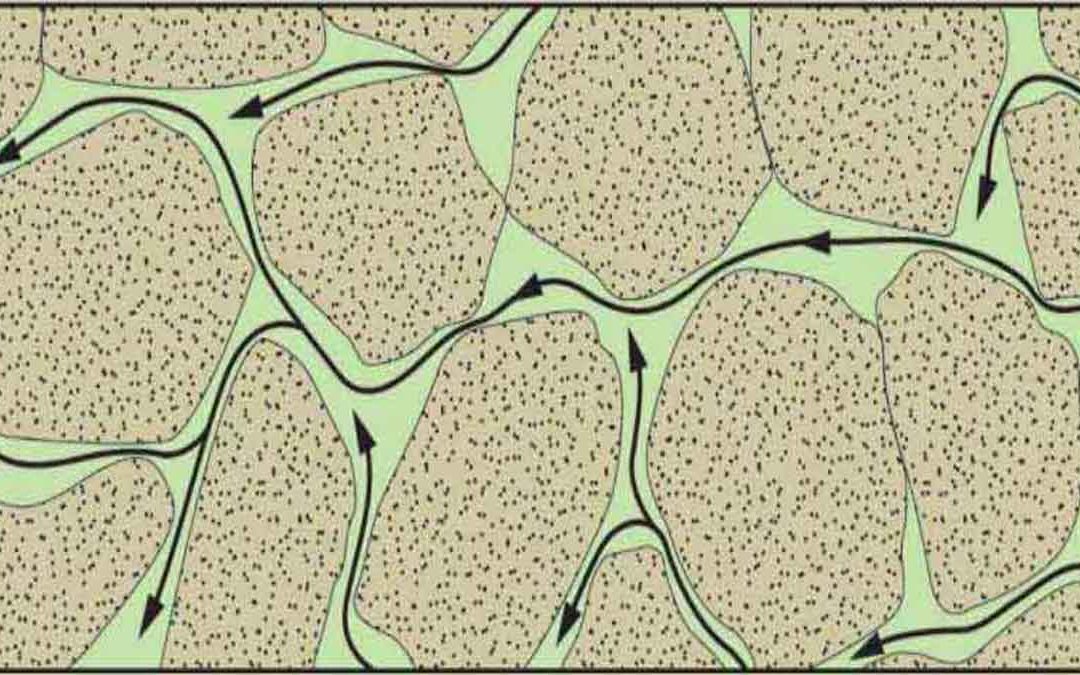
Permeability: Permeability is the ability of fluids to pass through a process material. It is measured in millidancy (MD) or Darcies (D) and expressed by k. According to Darcy’s law, Where, Q = Rate of fww K= Permeability (p1-p2) = Pressure drop across the sample A =...