by Gelogia Team | Nov 3, 2025 | Historical Geology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
Seismology is the study of earthquakes. Much of the information about the nature of faulting during an earthquake comes from the resulting seismograms. Most earthquakes occur due to plate motion, and understanding the direction and magnitude of this movement helps...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 31, 2025 | Structural Geology
A tunnel is a horizontal or slightly inclined underground passage that runs through rock or unconsolidated materials and remains open at both ends. Commonly circular, semicircular, or horseshoe-shaped, tunnels serve various purposes such as water conveyance,...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 27, 2025 | Petrology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
Joints are natural cracks or fractures in rocks that form when stress exceeds the rock’s strength. Unlike faults, they show little or no movement along the fracture. Joints typically appear in sets with regular patterns and result from factors like rock type, stress...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 21, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Stratigraphy, Structural Geology
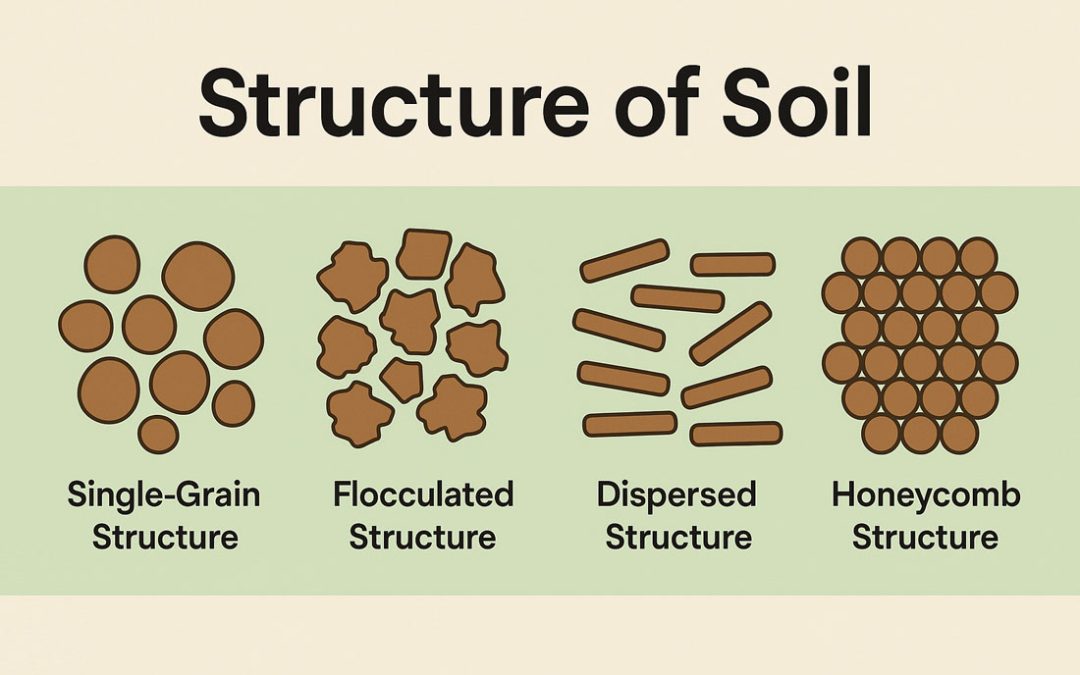
Soil structure refers to how soil particles arrange themselves within the matrix, which includes voids, fissures, and cracks. Several factors influence soil structure, such as the shape and size of particles, mineral composition, grain orientation, interactions...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 20, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
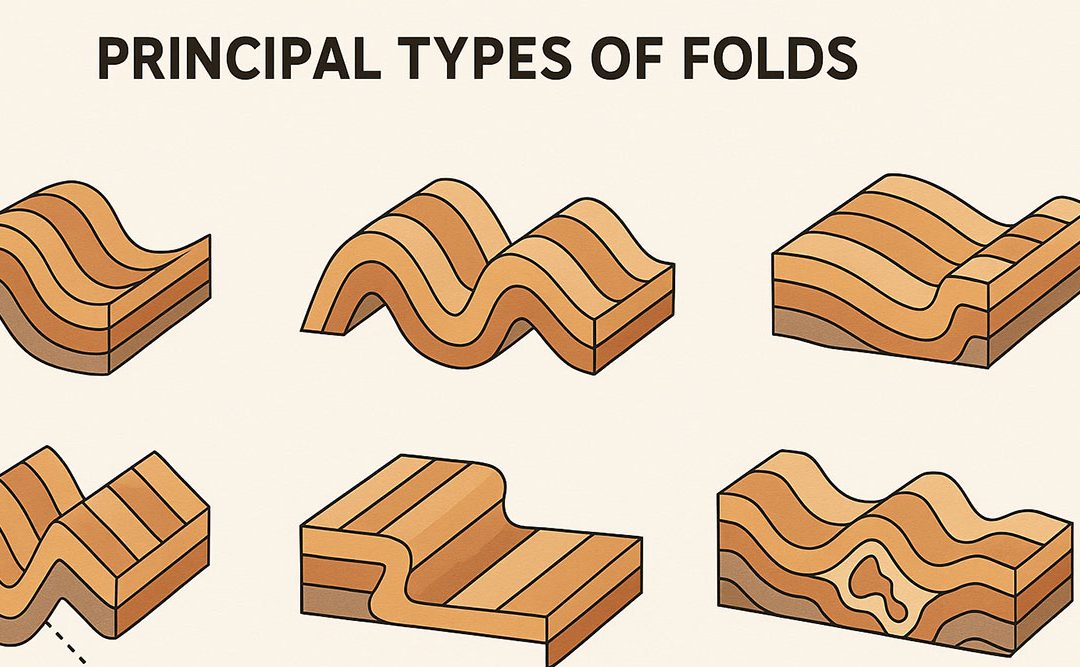
Folds are significant geological structures formed when rock layers undergo compression, resulting in bending without fracturing. They are commonly observed in deformed sedimentary, metamorphic, and even igneous rocks. Understanding the different types of folds and...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 19, 2025 | Structural Geology
Types of Bridges: There are five major types of bridges, namely Girder or Beam Bridge, Cantilever Bridge, Arch Bridge, Suspension Bridge, and Cable-Stayed Bridge. The magnitude of the load of the bridge and the forces acting on the support system considered in the...