by Gelogia Team | Jun 20, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
A seismograph is an essential device used by scientists to measure and record earthquakes. By understanding how seismographs work, we can better interpret seismic activity and improve earthquake preparedness. How Does a Seismograph Work? A seismograph is the device...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 19, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
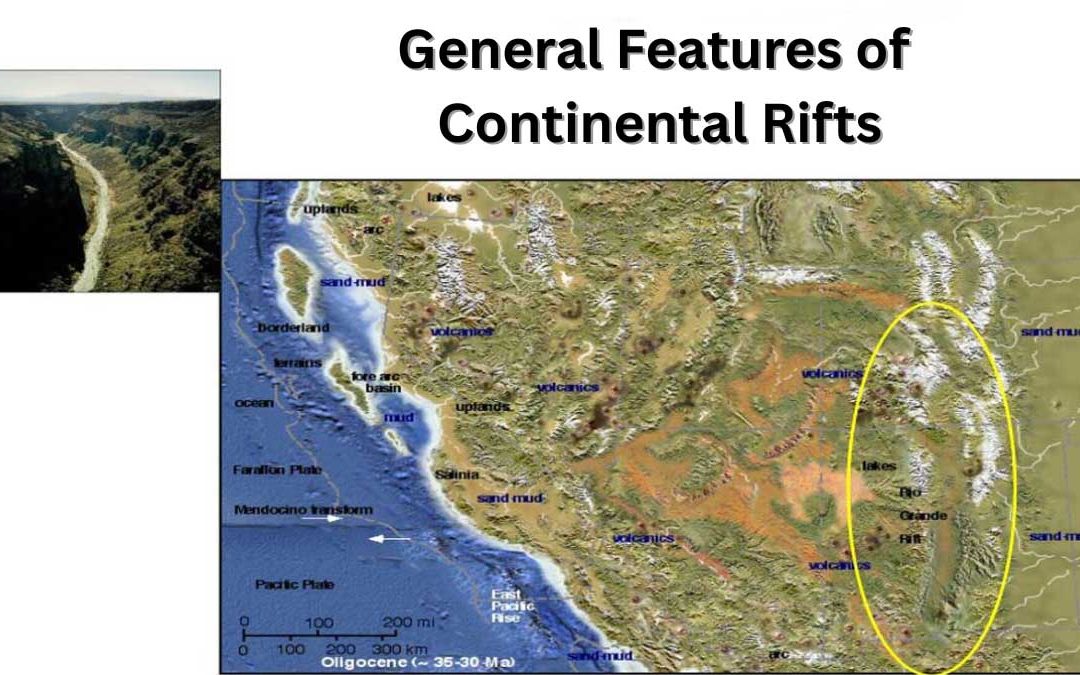
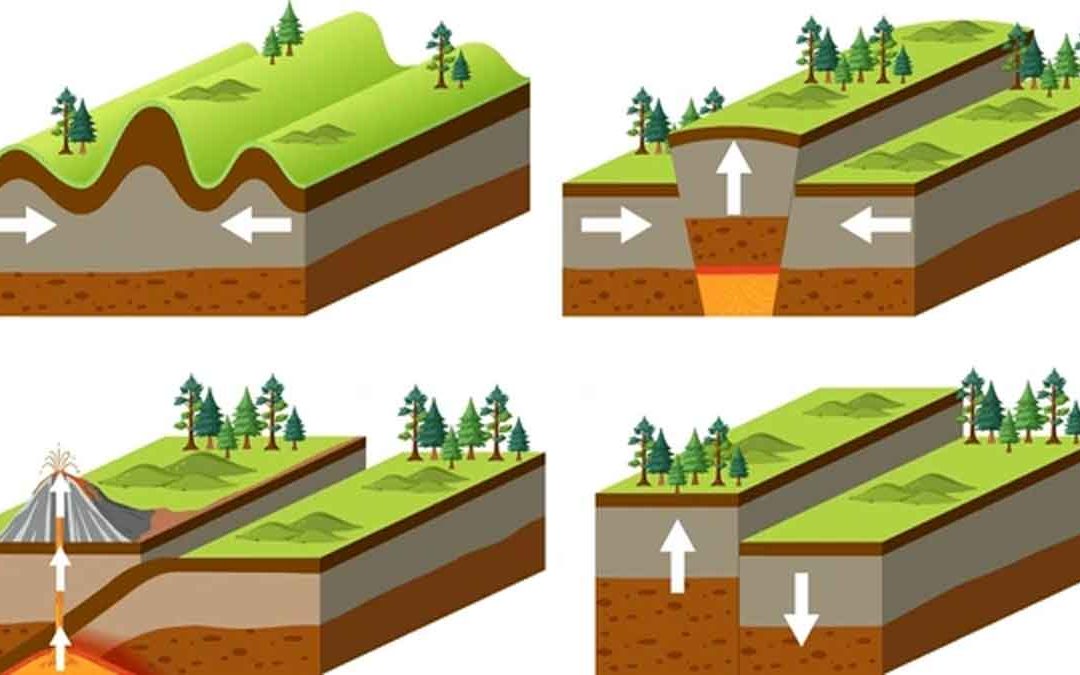
Continental rifts are geological zones where the Earth’s crust is stretched and broken, forming deep fault-bounded valleys. These structures play a key role in understanding plate tectonics, continental breakup, and the formation of new ocean basins. This...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 17, 2025 | Hydrology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology
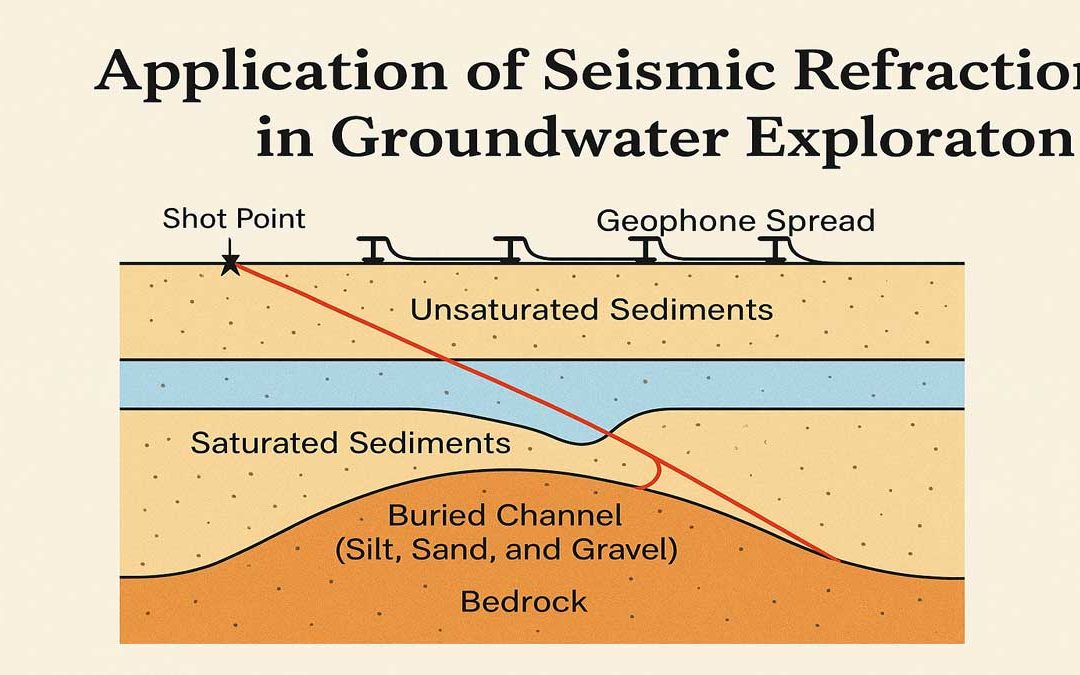
Application of Seismic Refraction Measurements in Groundwater: Mapping of Buried Channels using Seismic Refraction: The most common use of the seismic method in hydrogeology is the determination of the thickness of sediments overlying non-water-bearing consolidated...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 15, 2025 | Hydrology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology
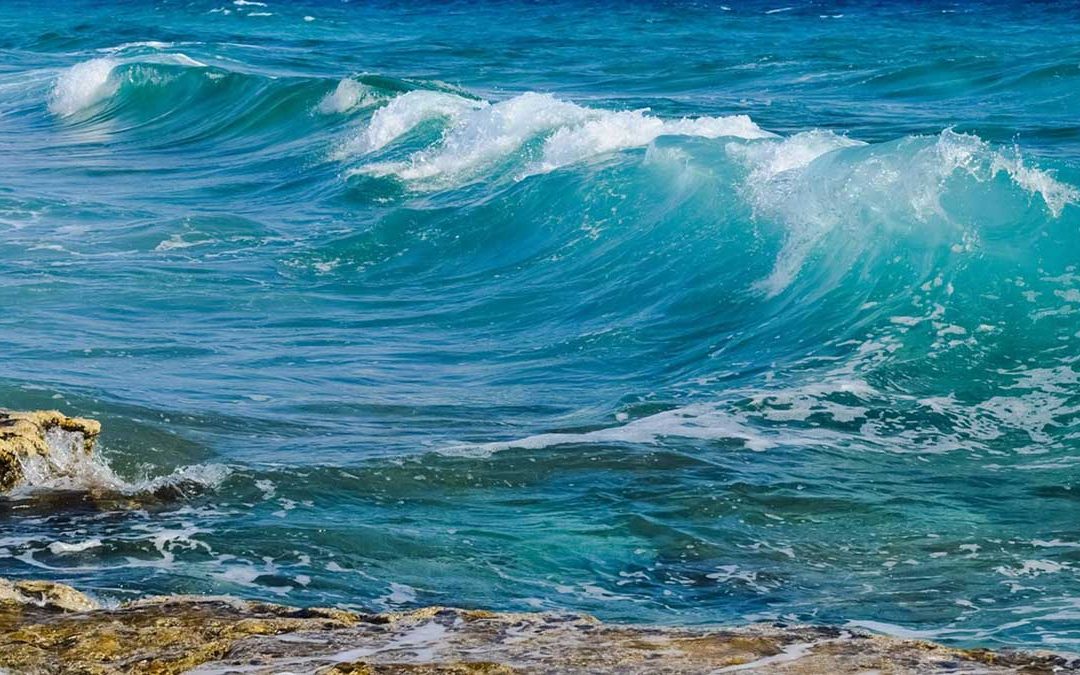
The energy that moves sand along a beach comes from the wind-driven water waves that break upon the shore. As wind blows over the surface of an ocean or a lake, some of the wind‘s energy is transferred to the water surface, forming the waves that move through the...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 12, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
Ophiolites: Ophiolites are tectonically emplaced successions of mafic and ultramafic rocks that are considered to represent fragments of oceanic or back-arc basin crust (Coleman, 1977; Moores, 1982). Units of Ophiolites: An ideal ophiolite includes from bottom to top...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 11, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
Convergent Margins: Convergent margins occur where the adjacent plates move toward each other and the motion is accommodated by one plate overriding the other. In plate tectonics, a convergent boundary, also known as a destructive plate boundary (because of...