by Gelogia Team | Jul 27, 2025 | Petrology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
Joints are natural cracks or fractures in rocks that form when stress exceeds the rock’s strength. Unlike faults, they show little or no movement along the fracture. Joints typically appear in sets with regular patterns and result from factors like rock type, stress...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 25, 2025 | Hydrology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology
Types of dams are classified based on construction materials and site conditions, each serving different engineering and environmental needs. The main types—concrete, masonry, rock-fill, and earth dams—store water, control floods, support irrigation, and generate...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 21, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Stratigraphy, Structural Geology
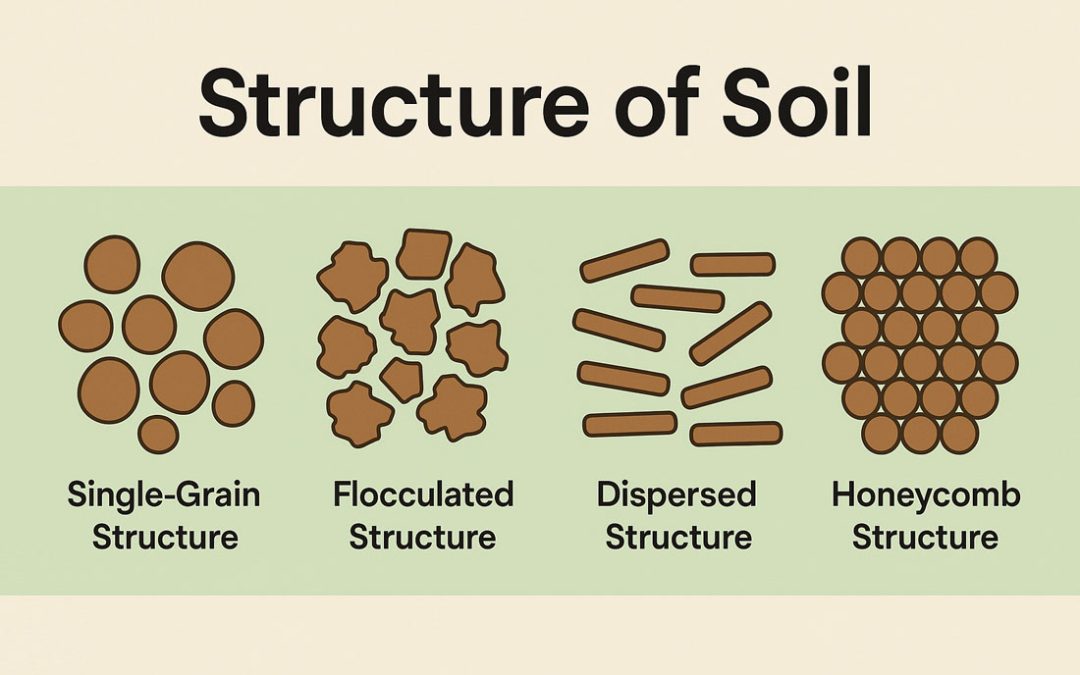
Soil structure refers to how soil particles arrange themselves within the matrix, which includes voids, fissures, and cracks. Several factors influence soil structure, such as the shape and size of particles, mineral composition, grain orientation, interactions...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 20, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
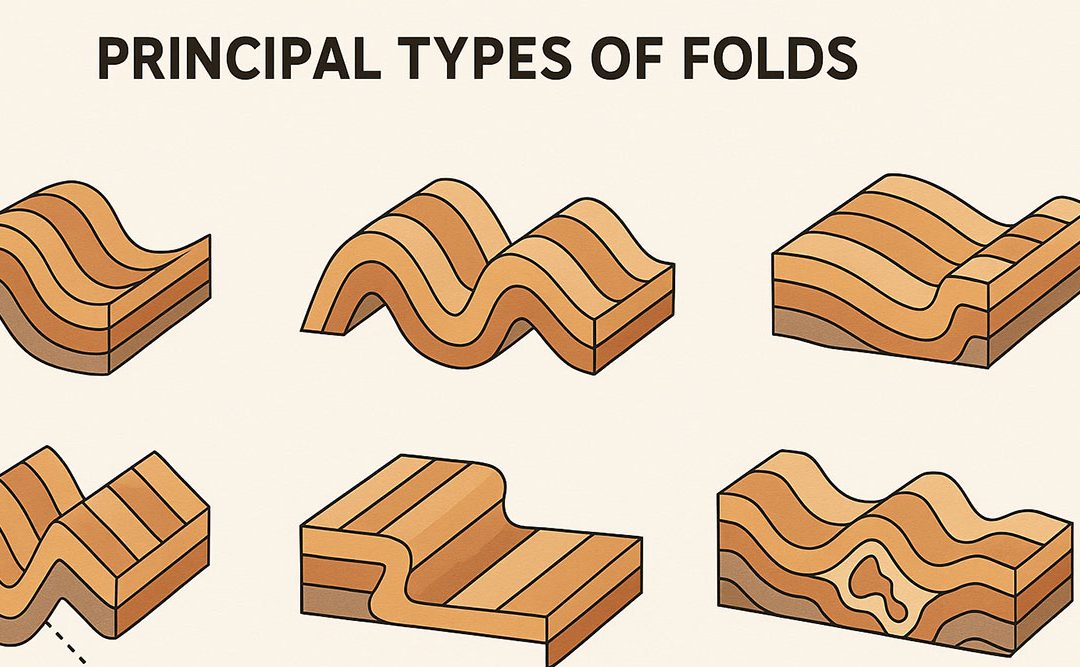
Folds are significant geological structures formed when rock layers undergo compression, resulting in bending without fracturing. They are commonly observed in deformed sedimentary, metamorphic, and even igneous rocks. Understanding the different types of folds and...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 19, 2025 | Historical Geology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology
James Hutton, usually described as the “Father of Modern Geology,” plays a critical role in the field of Earth sciences. His innovative insights contested prevailing perspectives on the Earth’s history and established the basis for contemporary...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 17, 2025 | Hydrology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
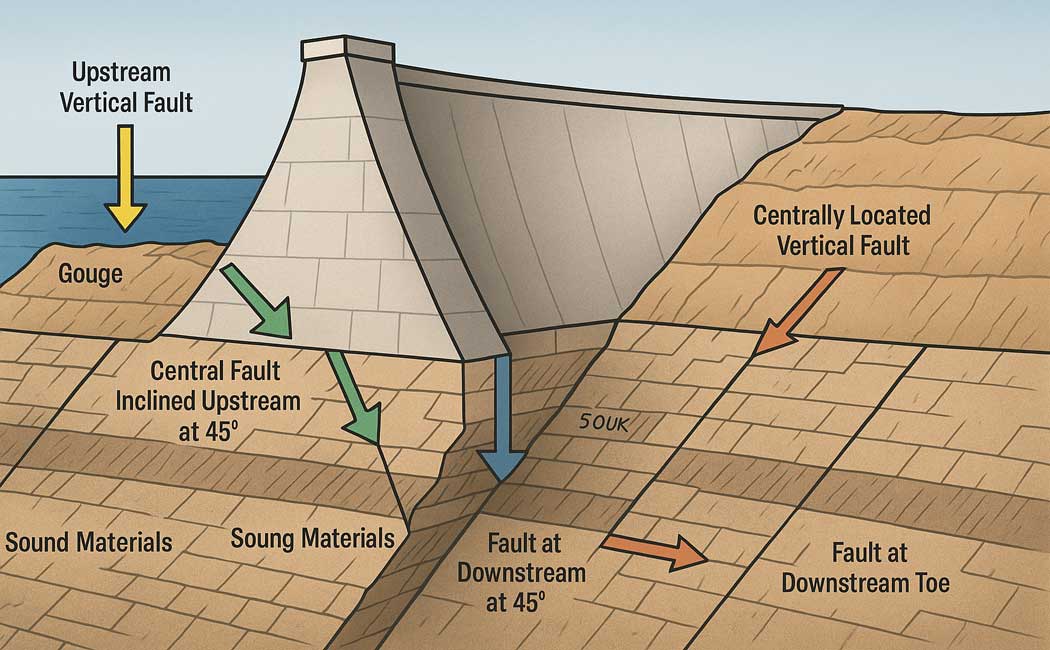
The fault zone lying under gravity dams is composed of weak gouge materials with a low modulus of elasticity as compared to sound rocks, and hence is more deformable. The pressure of a fault zone induces more stress in a foundation than a normal foundation. A fault...