by Gelogia Team | Jan 11, 2026 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
Renewable natural resources play a vital role in sustaining life and supporting economic development. Understanding their key characteristics helps in managing them wisely and ensuring their availability for future generations. Characteristics Of Renewable Natural...

by Gelogia Team | Nov 9, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
The Mercalli scale was developed in 1902 and modified in the 1930s. The Mercalli scale assigns a numerical value, from Roman numeral I to XII, to the intensity of seismic shaking at any one particular location. Modified Mercalli scale: I. Not felt, except by a very...

by Gelogia Team | Nov 3, 2025 | Historical Geology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
Seismology is the study of earthquakes. Much of the information about the nature of faulting during an earthquake comes from the resulting seismograms. Most earthquakes occur due to plate motion, and understanding the direction and magnitude of this movement helps...

by Gelogia Team | Aug 3, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
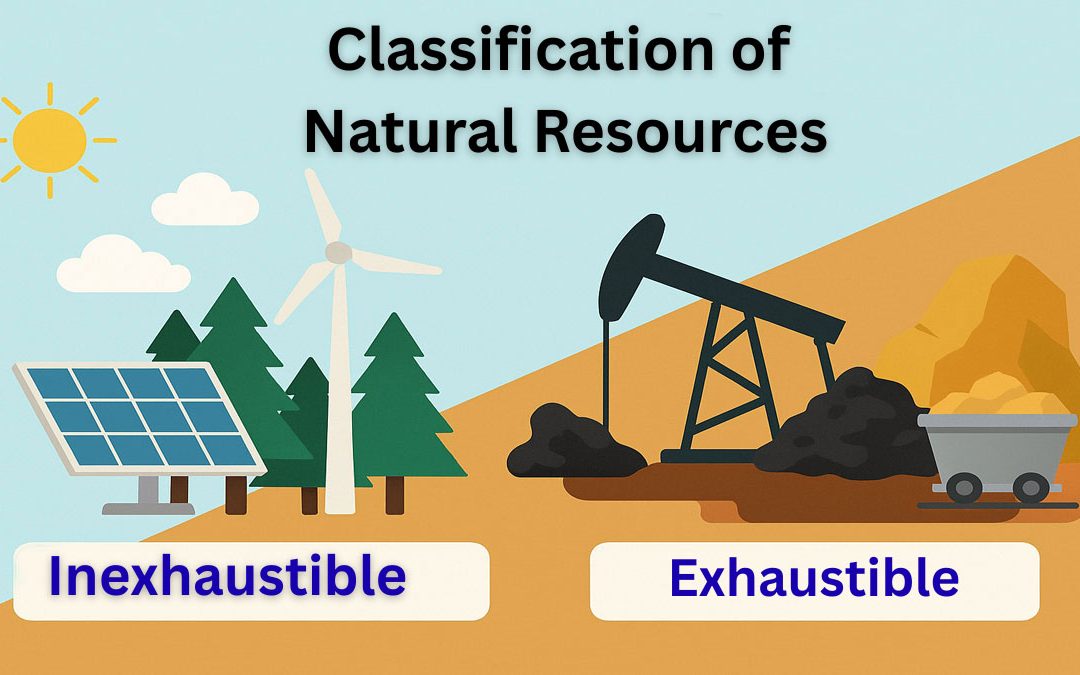
The classification of natural resources is essential because natural resources vary greatly in their location, quantity, and quality. For instance, a particular forest type may occur only in certain countries. Also, the geographical area covered by the forest and the...

by Gelogia Team | Aug 1, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
The density of soil refers to the mass of soil within a given volume. It helps us understand how compact or loose the soil is, which is important for construction, farming, and soil testing. Different types of soil density, like bulk density, dry density, saturated...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 28, 2025 | Hydrology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology
A tsunami is one of nature’s most powerful and destructive forces, causing immense devastation along coastal regions. Unlike ordinary tidal waves, tsunamis are triggered by undersea earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or seabed movements. These events send high-speed...