by Gelogia Team | Feb 27, 2025 | Paleontology
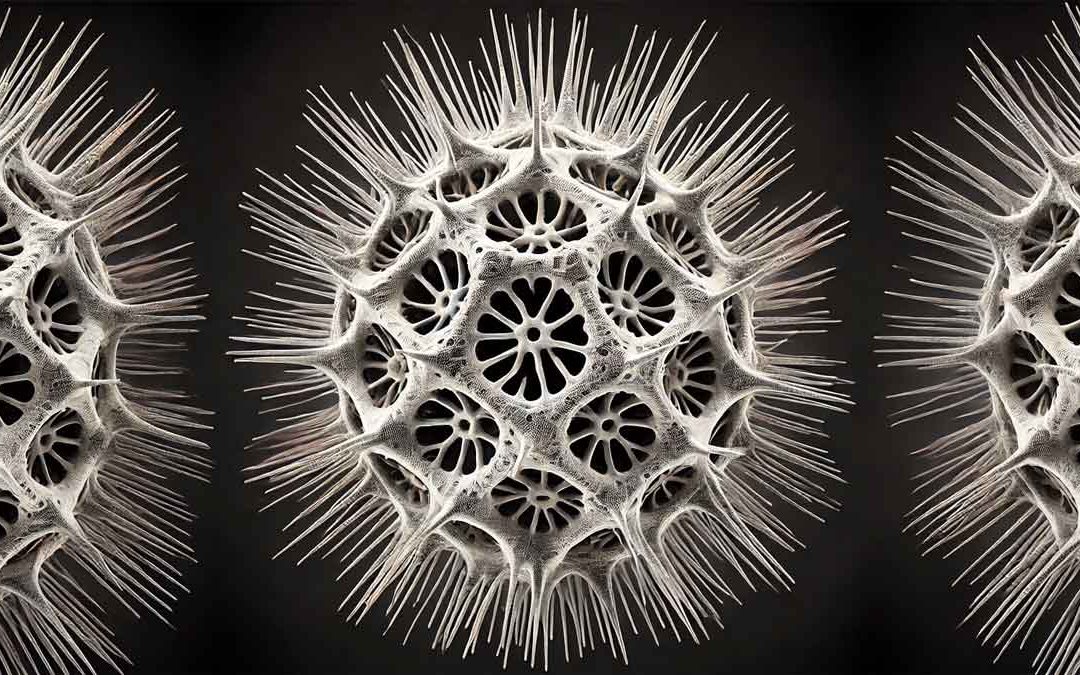
Radiolaria: Radiolaria are free-floating protists with roughly spherical cells and thread-like pseudopodia extending radially over a delicate endoskeleton. Moder Radiolarians are marine with representatives in Cambrian times. Radiolarians provide the most useful data...

by Gelogia Team | Feb 26, 2025 | Paleontology
Applications of palynology: Biostratigraphy & geochronology: Geologists use palynological studies in biostratigraphy to correlate strata & determine the relative age of given bed or stratigraphic sequences. Paleoecology & climate change: Reconstructing...

by Gelogia Team | Feb 24, 2025 | Paleontology
Classification of Living Fossils: Living fossils are classified by two main characteristics. Living organisms that are members of a taxon that has remained recognizable in the fossil record over an unusually long time span. They show little morphological divergence,...

by Gelogia Team | Feb 24, 2025 | Paleontology
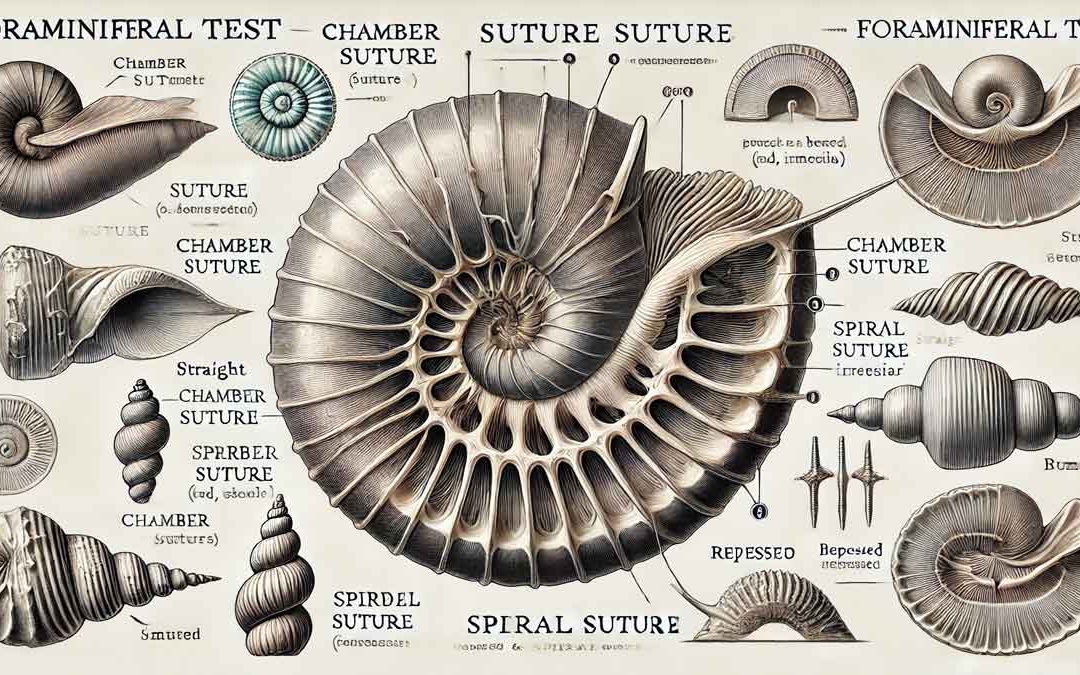
Suture: The suture is the position on the surface of the test where the septa join the wall of the test. With reference to the surface of the test, the sutures can either be depressed, lie in the same plane, or above the surface of the test. Thickened sutures are...

by Gelogia Team | Feb 23, 2025 | Paleontology
The Ecological Factors of Foraminifera: The ecological factors that control the distribution of foraminifera in marine environments are: Food: Foraminifera plays a prominent role in marine ecosystems as micro omnivores. They feed on- (a) Protozoa, (b) algae,...

by Gelogia Team | Feb 22, 2025 | Paleontology
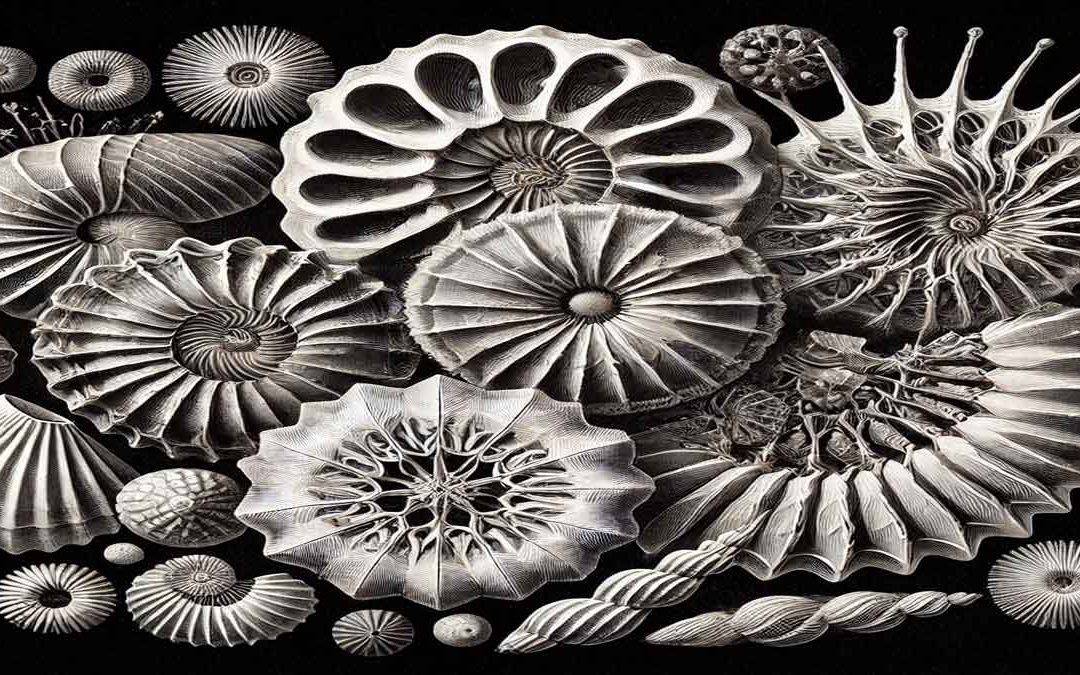
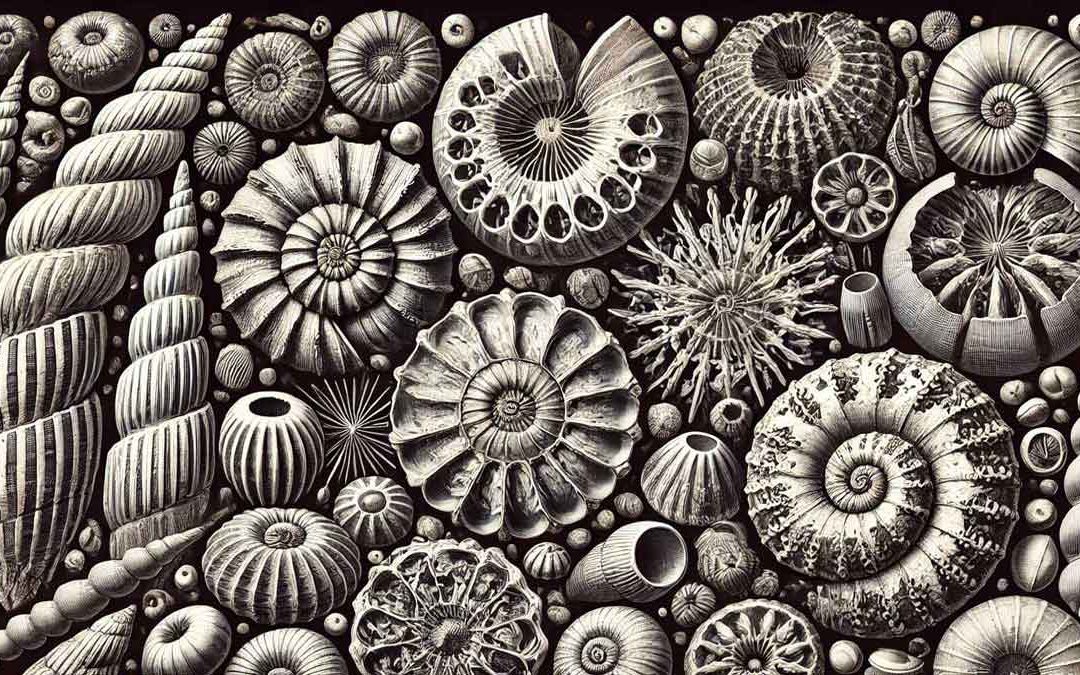
Foraminifera are tiny, single-celled organisms with intricate shells called tests, made of calcium carbonate or agglutinated particles. These marine microorganisms are essential in geology and environmental science, helping date rock layers, track climate changes, and...