by Gelogia Team | Jul 28, 2025 | Hydrology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology
A tsunami is one of nature’s most powerful and destructive forces, causing immense devastation along coastal regions. Unlike ordinary tidal waves, tsunamis are triggered by undersea earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or seabed movements. These events send high-speed...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 25, 2025 | Hydrology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology
Types of dams are classified based on construction materials and site conditions, each serving different engineering and environmental needs. The main types—concrete, masonry, rock-fill, and earth dams—store water, control floods, support irrigation, and generate...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 17, 2025 | Hydrology, Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
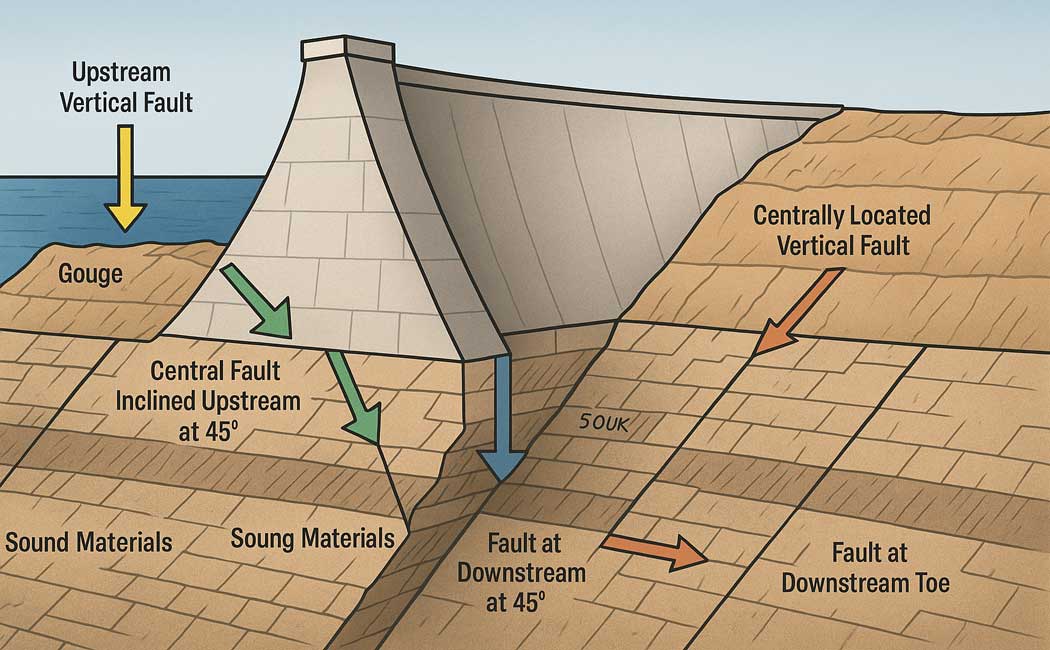
The fault zone lying under gravity dams is composed of weak gouge materials with a low modulus of elasticity as compared to sound rocks, and hence is more deformable. The pressure of a fault zone induces more stress in a foundation than a normal foundation. A fault...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 13, 2025 | Hydrology
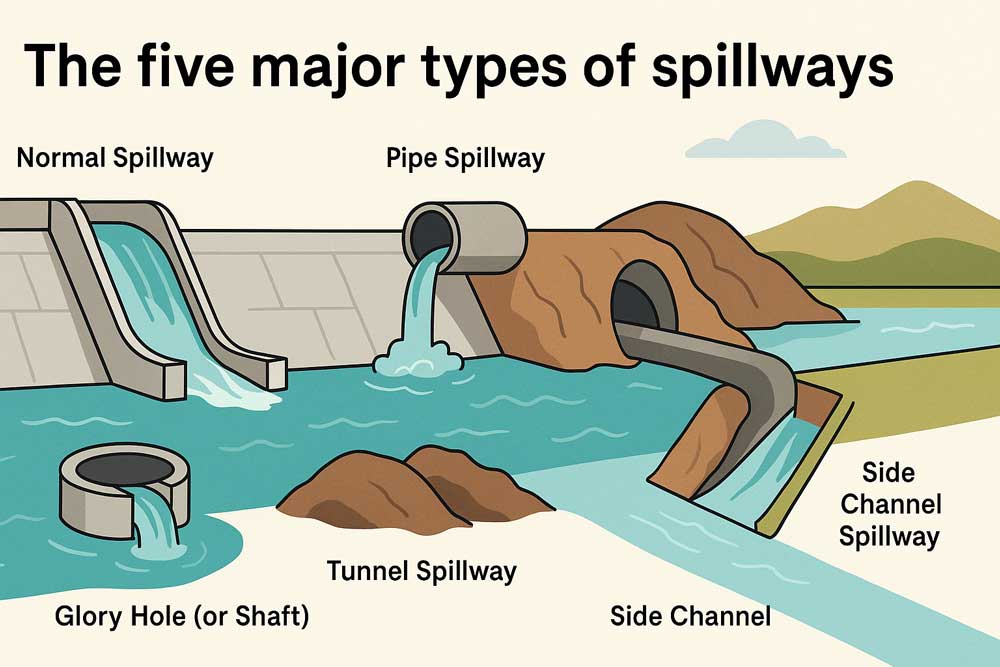
Spillways discharge water from upstream to downstream and represent the most essential structures for dams to function properly (Fig. 1). They release flood water without causing damage to the dam. The spillway often forms an integral part of the dam, constructed...

by Gelogia | Jul 4, 2025 | Hydrology
A material is permeable if it contains continuous voids. All materials, such as rocks, concrete, soils, etc., are permeable. The flow of water through all of them obeys approximately the same laws. Hence, the difference between the flow of water through rock or...

by Gelogia Team | Jun 18, 2025 | Hydrology
Bangladesh heavily depends on groundwater for irrigation, drinking water, and industrial uses. However, overextraction, pollution, and poor governance have put this vital resource at risk. To protect water security for future generations, sustainable groundwater...