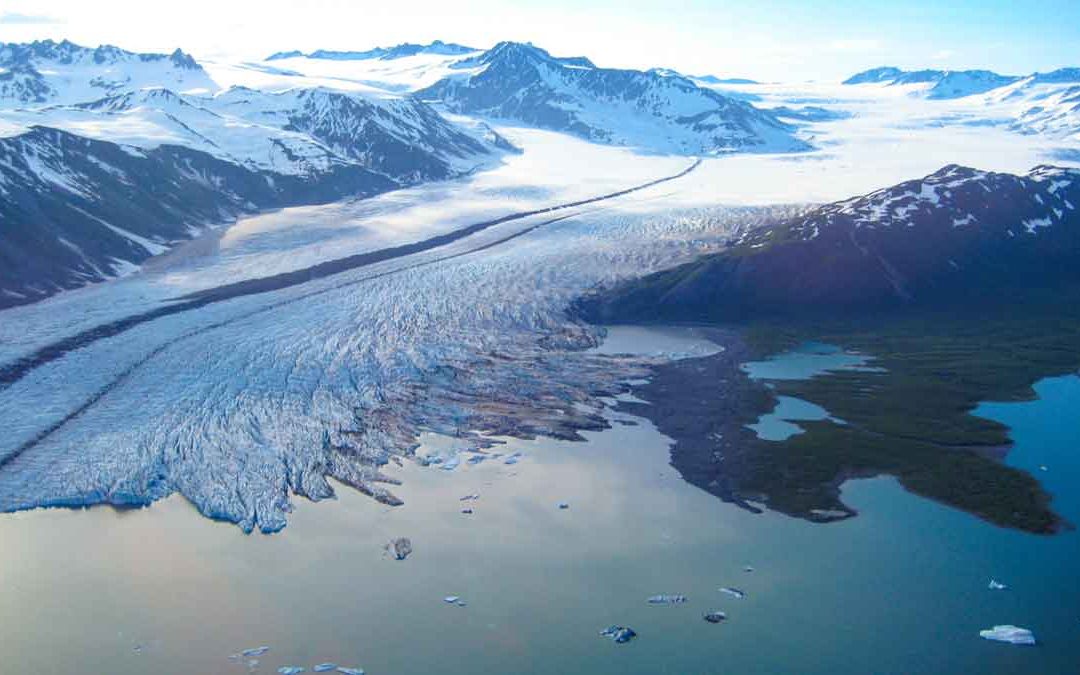
Glacial landforms are the result of the dynamic processes involving glaciers as they move and melt. These features can be categorized into three main types: constructional, ice-contact, and proglacial. Each type emerges through distinct glacial activities, such as the deposition of ice, the flow of meltwater, and the accumulation of sediment.
Types of Glacial Landforms:
There are three categories of glacial landforms,
1) Constructional landforms
2) Ice-contact landforms
3) Proglacial landforms
Constructional landforms:
Direct action of ice resulted in the constructional landform or morainic landforms. Behind the end moraines of the ice front, there is lodgement till. These lodgement tills form gently undulating or flat plains, known as till plains or ground moraine flats.
A special depositional form found in the lodgement zone behind the end moraines is the drumlin. Ideally, drumlins are streamlined, oval, asymmetrical hills, varying greatly in size and shape from about 100 to 2000 yards long, 50 to 500 yards wide, and 20 to 200 feet high.
Drumlins are found in the zone of deposition immediately behind end moraines, which indicates that they were formed by actively advancing ice. End moraines are of different kinds, such as, push-moraines, hummocky end-moraines, interlobate moraines, block moraines etc. Further descriptions of these end-moraines are referred to the book R.G. West, 1974.
Ice-contact landforms:
These landforms are two kinds: 1) landforms associated with the ice-contact slope sediments, and 2) the kettle or kettle-hole. These kettle-holes were formed by the melting of a block of ice. The most important landforms are Kame terrace, Ice-contact slope of terrace with kettle hole, Crevasse-fillings, Esker, Kame, and Moulin kame.
There are more or less parallel to the direction of the ice movement. These are formed by the bedload sediments of the meltwater paleochannel flowing on top of the ice sheets. After deglaciation, the bedload sediments form such an elevated ridge. The eskers are more or less symmetrical.
Kames are low hills with steep slopes. They are formed by the ice contact stratified drift. Kame terraces are formed laterally to the ice sheet by meltwater streams. For further discussion, refer to the book by R.G. West (1974.
Proglacial landforms:
The meltwater from the ice sheet flows over a floodplain and ultimately discharges into the sea or a lake basin. This plain is called an Outwash plain, and the furthest point near the lake or sea where the meltwater discharges into the sea is called the Distal slope.
Glacio-fluvial sediments are deposited in the outwash plain. Far to the distal slope, near the sea, a glaciotectonic environment prevails. Under the heading of proglacial landforms, beaches, terraces, bars, and lake-clay flats can be cited.