Geology is a fundamental scientific discipline that provides important insights into Earth’s history, structure, and processes. This is important because we use many of these elements daily. We need to understand how geological processes (such as plate tectonics, earthquakes, etc.) have affected our lives and will continue to affect them. Geologists are critical in numerous fields, including natural resource exploration, environmental protection, and hazard assessment. Whether locating valuable mineral deposits or predicting earthquakes, geologists use their expertise to safeguard our planet and its inhabitants.
So, join us as we delve into the world of geology, discovering its wonders and the vital role geologists play in unraveling the mysteries of our Earth.
What is Geology?
Geology is the branch of science that seeks to describe and understand the Earth’s composition, behavior, and history, including the evolution of life on Earth and the continuing interaction of life and the solid Earth.
Geology is the science concerned with the study of planet Earth, the materials that compose it, the processes that transform those materials from one form to another, and the stories those materials tell; the forces that deform the Earth’s outer layers, forming ocean basins and continents; the processes that transform the Earth’s surface; and the application of geological knowledge to search for valuable materials and understand the relationship between geological processes and people.
Importance of studying geology:

Understanding how the world works is essential for every person. Studying geology is important beyond merely securing a fulfilling career, although it certainly provides that benefit. Every object and phenomenon in the world is associated with geological concepts. The importance of imparting geological knowledge to teachers at all levels, from primary to secondary institutions, colleges, and universities, should be emphasized. This is justified because such knowledge is relevant for all people.
This is why geology is important or why you should study geology.
- It provides geologists the skills to identify, investigate, and utilize natural resources such as metals, groundwater, and fossil fuels, facilitating our population growth and meeting technological needs.
- Geologists can predict and develop mitigation measures by studying hazards such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, hurricanes, floods, tsunamis, and slides. These hazards often destroy infrastructure and kill animals and people.
- Geologists collaborating with other researchers can improve their understanding of climate dynamics and develop strategies to combat climate change. Climate change is a complex challenge that demands our immediate attention.
- Geologists possess a deep understanding of the Earth and are uniquely qualified to develop strategies to conserve the planet by reducing pollution and environmental degradation. Their initiatives may include conversion to renewable and geothermal energy sources. Furthermore, reducing carbon gas emissions is essential, as they contribute significantly to global warming.
- Understanding geology can help conserve soil and guarantee that the land will be agriculturally productive.
Who is a geologist?
Geologists study the Earth: its history, nature, materials, and processes. There are many types of geologists: environmental geologists, who study the impact of humans on Earth’s systems, and economic geologists, who explore and develop the Earth’s resources, are just two examples. Additionally, there are engineering geologists, geomorphologists, geophysicists, mineralogists, geochemists, glacial geologists, structural geologists, petrologists, sedimentologists, hydrogeologists, etc. A career in geology offers a wide range of opportunities for anyone interested in the Earth and how it works.

The Role of a Geologist:
A geologist plays a vital role in understanding the Earth’s processes, materials, and history. They study the Earth’s crust’s structure, composition, and physical properties to identify and manage natural resources such as minerals, oil, and gas. Geologists assess natural hazards such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and landslides, helping to reduce risks to human life and property. Additionally, they contribute to environmental protection by assessing soil and water quality and guiding land use and waste management practices. Their work is essential to advancing scientific knowledge and supporting sustainable development.
Geologist Responsibilities and Duties:
- Perform geologic and field operations using established and analytical geologic methods.
- Develop and analyze geologic structures and maps.
- Stay up to date with geological theory and principles.
- Perform field sampling and analyze sample data for geologic settings.
- Perform geological analysis and perform geophysical and geotechnical tests.
- Guide junior geologists as needed.
- Prepare reports on completed fieldwork and findings.
- Accurately analyze and classify soil and rock.
- Supervise field technicians during fieldwork and investigations.
- Follow health and safety practices to avoid accidents.
Career opportunities in geology:

A career in geology offers a variety of opportunities across different specialties. Exploration geologists are critical to discovering new mineral deposits and energy resources, using advanced technology to locate these resources efficiently. Hydrogeologists focus on groundwater management, ensuring sustainable water supplies in areas facing scarcity and growing concern as global demand increases and climate change affects availability.
Engineering geologists collaborate with civil engineers to evaluate ground conditions for construction projects, ensuring the stability and safety of structures such as dams and highways. Environmental geologists deal with pollution, plan land reclamation, and reduce the environmental impacts of industrial activities, promoting sustainable development.
In academia, geologists advance scientific knowledge through research and teaching. They explore Earth history, climate evolution, and natural disasters, and their findings often influence public policy. The emerging field of geoinformatics combines geology with data science, analyzing geological data using GIS and remote sensing to aid decision-making in various fields.
Paleontology, another branch of geology, studies fossils to understand past life forms and predict future biodiversity trends. The broad scope of geology allows professionals to specialize in areas that align with their interests, which play an essential role in managing Earth’s resources and environmental challenges.
What does Geology Entail?
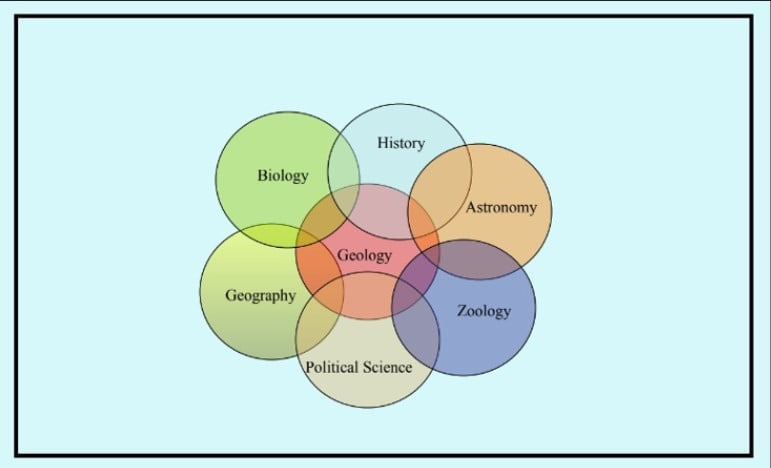
A Venn diagram showing the intersection of the various sciences that are part of the study of geology.
Conclusion:
Geology provides a guide to Earth’s past and its future. By understanding the processes that shape our planet, we appreciate its beauty and gain important insights for managing resources and mitigating natural hazards. As we continue to explore and study geology, we connect more deeply with the story of our world and our role in preserving it for future generations.






