Deviatoric Stress or Directed Pressure:
Deviatoric stress is produced by tectonic forces in the Earth, such as plate motions; this pressure brings about change to produce foliations and lineation’s.
This is commonly represented in terms of three stress values in the three principal stress directions (01, 02, 03, where is the stress in the direction of maximum compressive stress, is the stress in the direction of minimum compressive stress, and is the stress in the direction that is orthogonal to σ1 and 03). The extensional stress would act along the direction of minimum principal stress.
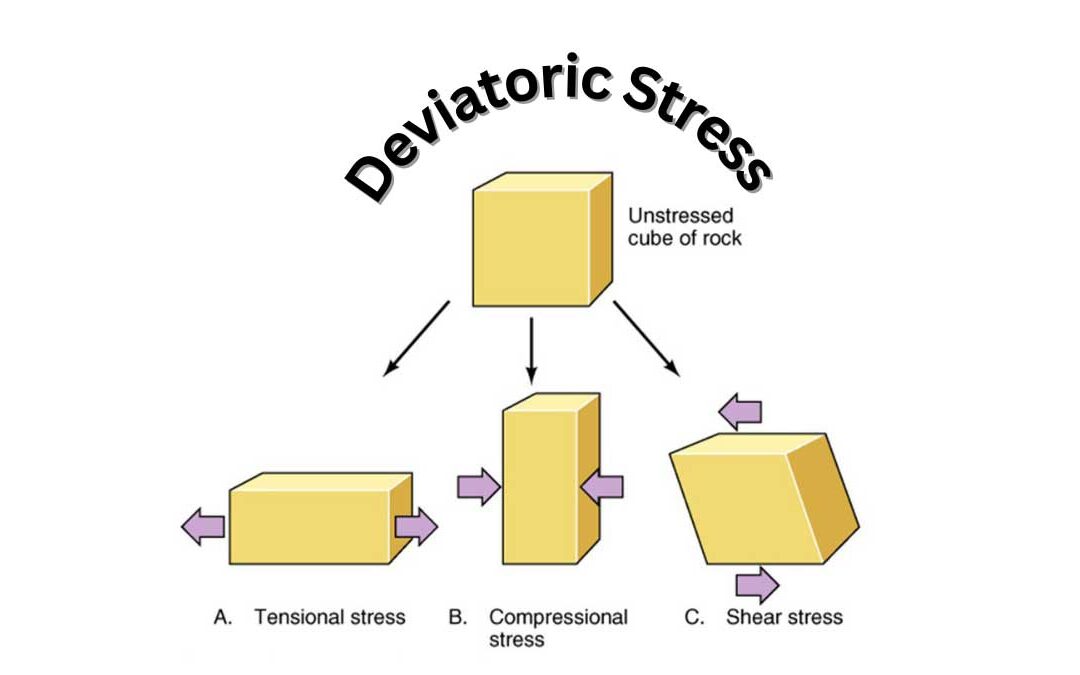
Types of Deviatoric stresses:
Deviatoric stresses are of three types. They are:
- Tension
- Compression
- Shear
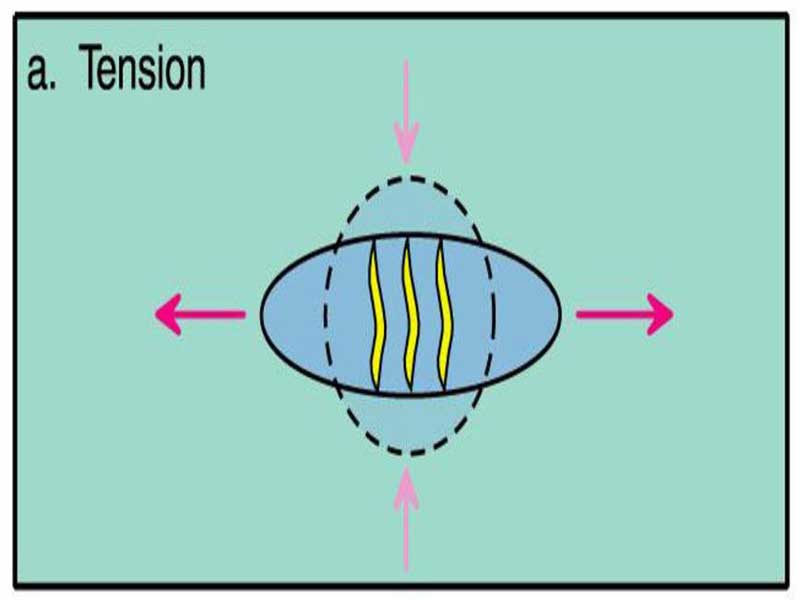
Tension:
In tension is negative, and the resulting strain is extension, or pulling apart. Tension fractures may open normally to the extension direction and become filled with mineral precipitates.
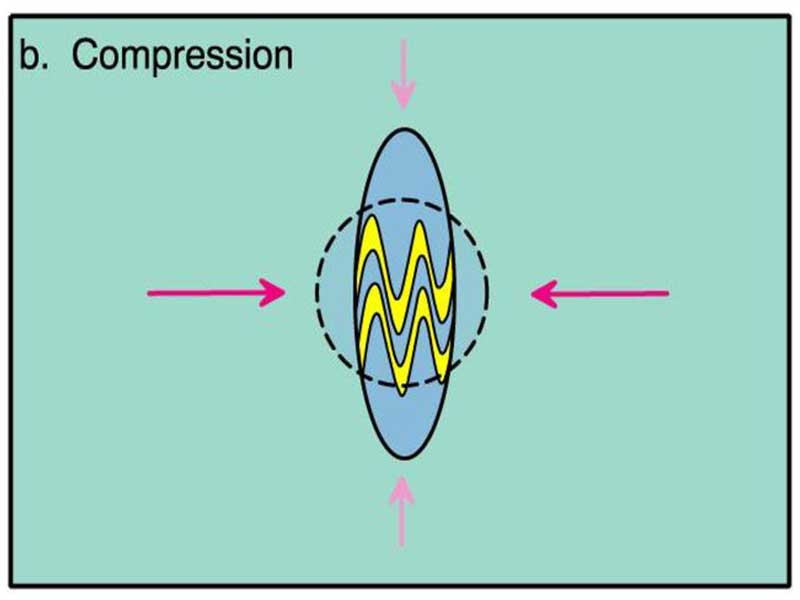
Compression:
Compression is dominant. Compression causes flattening or folding. Folding produces more homogeneous flattening.
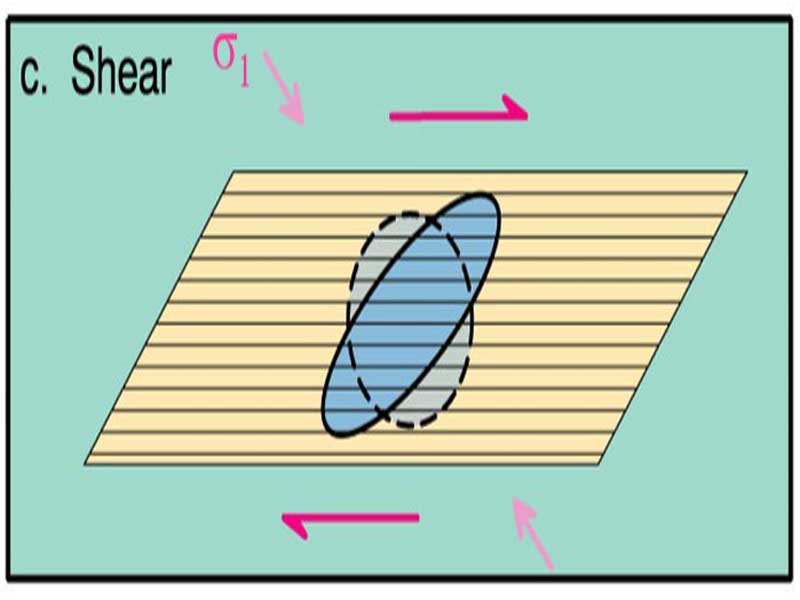
Shear:
Shear motion occurs along planes at an angle to Shear, causing slip along parallel planes and rotation.