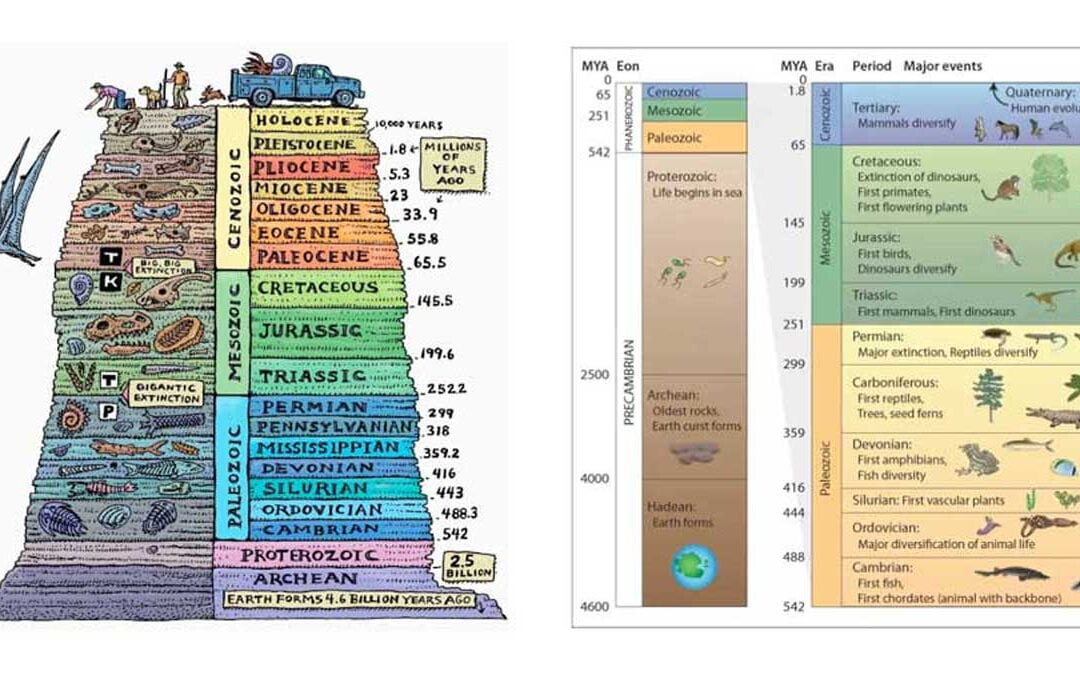
What is the Geological Time Scale?
The geological time scale is a system geologists use to subdivide the great span of time since the origin of the Earth. In other words, when the duration (time range) of the division in the geological column is given in terms of years, the arrangement is called “Geological time scale.”
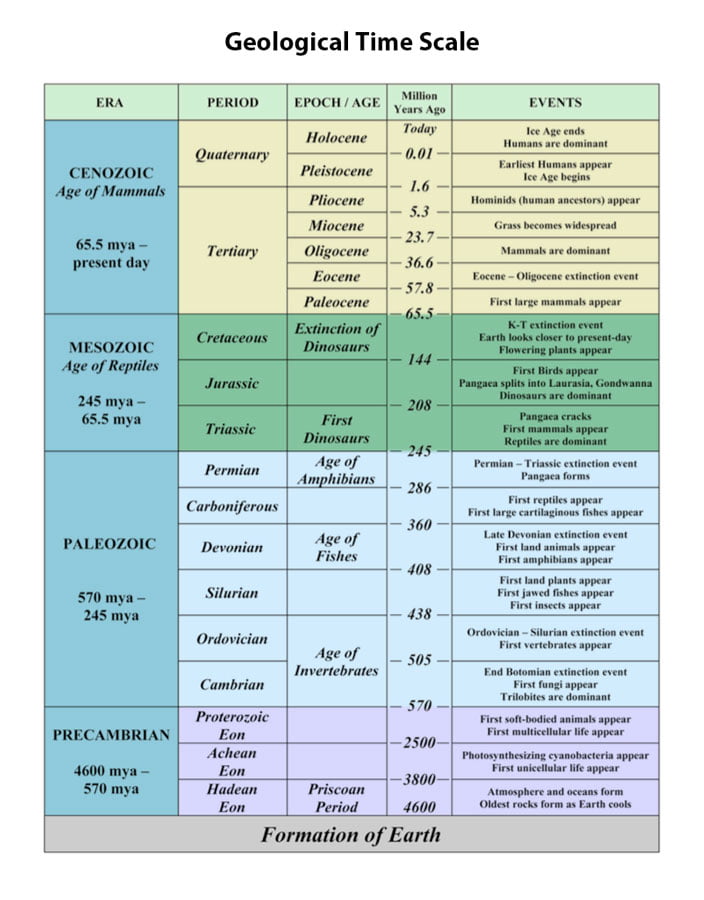
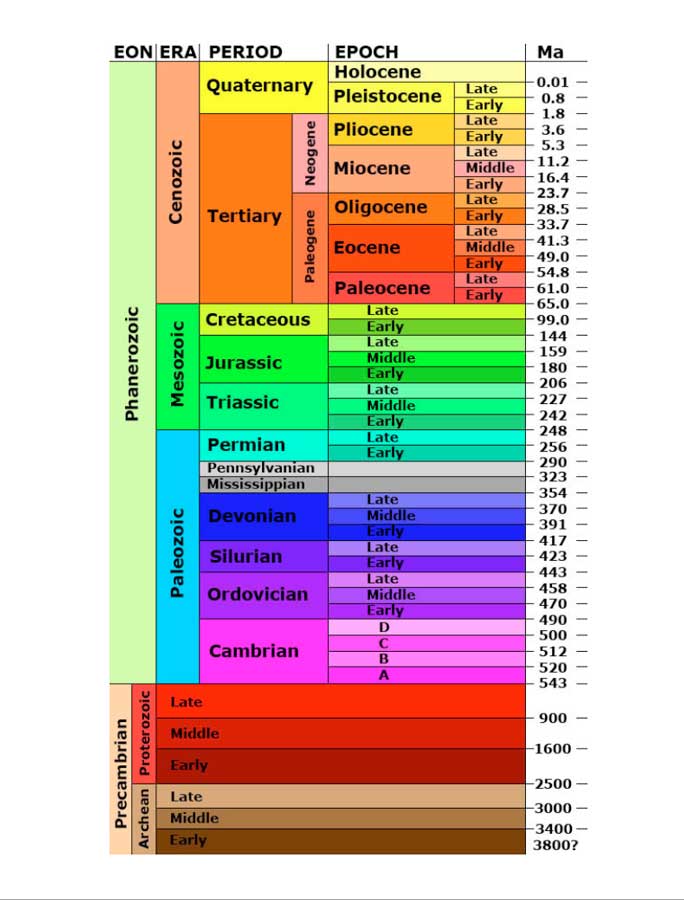
Geologic Time Scale EON
EON is the largest unit on the geologic time scale. It’s also called eonothems. There are two EONs on the time scale.
- Precambrian (Oldest): 4.6 billion Years to 543 million Years
- Phanerozoic (Youngest): 543 Years to Present
Geologic Time Scale ERA
ERA is the second largest unit on the geological time scale. For the Phanerozoic EON, there were three ERAs.
- Cenozoic (Younger): 65 million years to present
- Mesozoic: 248 million to 65 million
- Paleozoic (Older): 543 million 248 million
Geologic time scale Periods
The Geologic time scale Period is the smallest unit of Geologic ERA.
- Quaternary (Younger): 1.8 million to present
- Tertiary: 65 million to 1.8 million years
- Cretaceous: 114 million to 65 million years
- Jurassic: 206 million to 144 million years
- Triassic: 248 million to 206 million years
- Pennsylvanian: 323 million to 290 million years
- Mississippian: 354 million to 354 million years
- Devonian: 417 million to 354 million years
- Silurian: 443 Ma to 417 Ma
- Ordovician: 490 Ma to 443 Ma
- Cambrian (Older): 543 Ma to 490 Ma
Geologic EPOCH
EPOCH is the smallest time unit on the geological time scale.
- Holocene (Younger): 0.01 Ma to present
- Pleistocene: 1.8 Ma to 0.01 Ma
- Pliocene: 5.3 Ma to 1.8 Ma
- Miocene: 23.7 Ma to 5.3 Ma
- Oligocene: 33.7 Ma to 23.7 Ma
- Eocene: 54.8 Ma to 33.7 Ma
- Paleocene (Older): 65 Ma to 54.8 Ma
The Earth timeline refers to the chronological history of our Earth from its formation to the present. Earth formation started 4.6 billion years ago.
There are four units. EON, ERA, PERIOD and EPOCH.