by Gelogia Team | Jul 11, 2025 | Crystallography & Mineral Optics, Physical Geology & Geomorphology
The classification of minerals is primarily based on their chemical composition, which allows scientists and geologists to systematically organize them into distinct groups. Minerals may be classified based on their chemical composition. They are grouped and described...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 10, 2025 | Mineralogy, Physical Geology & Geomorphology
Clay minerals consist of crystalline materials that give soil its plasticity and cohesion. A clayey soil, along with non-clay minerals like quartz, feldspar, mica, and calcite, often includes one or two clay minerals made of microscopically thin sheets. Chemically,...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 9, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology
The structure of soils is the arrangement of the constituent particles in the soil matrix that contains voids, fissures, and cracks. Soil structure depends on many factors such as shape, size, mineral composition, orientation of the grains, the relation of soil water...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 7, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
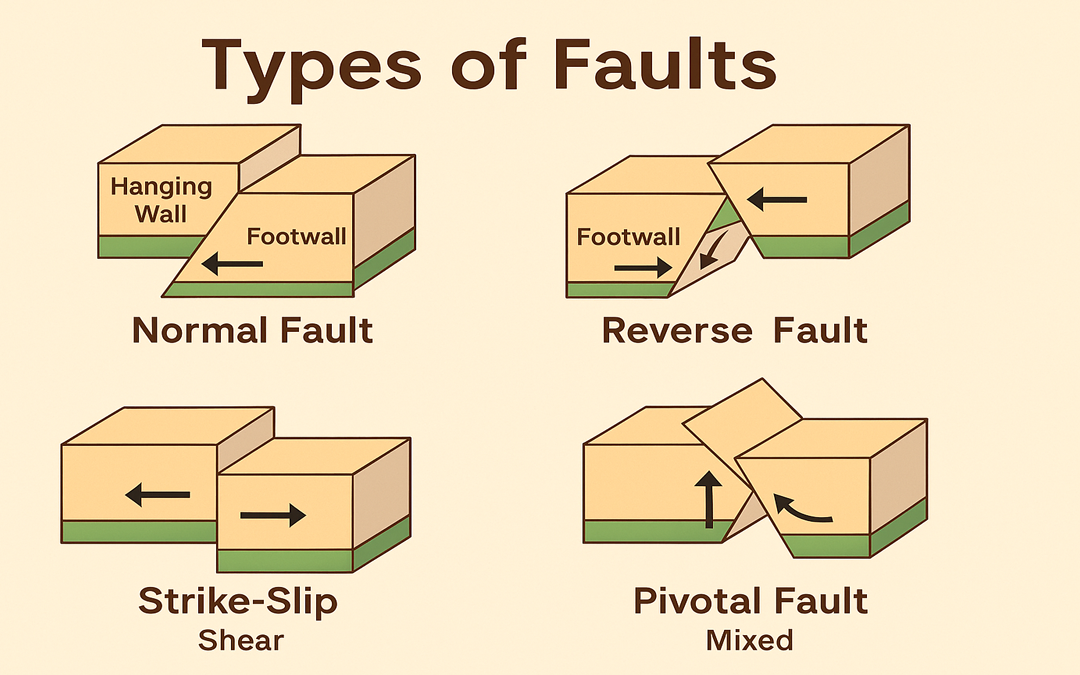
Faults are fractures in the Earth’s crust where blocks of rock have moved past each other due to tectonic forces. These movements are caused by stresses such as compression, tension, and shearing. Understanding the types of faults is essential in geology to interpret...

by Gelogia Team | Jul 6, 2025 | Physical Geology & Geomorphology, Structural Geology
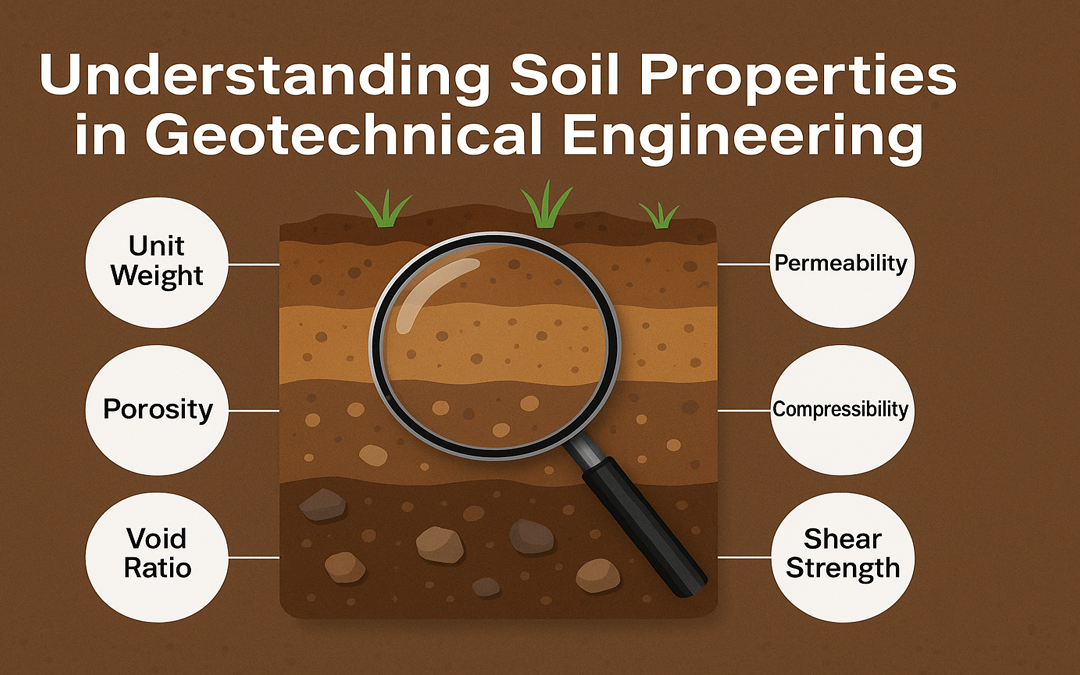
Soil properties are fundamental characteristics that define how soil behaves under various conditions. In geotechnical engineering, understanding these properties is essential for analyzing ground stability, designing foundations, and ensuring safe construction...