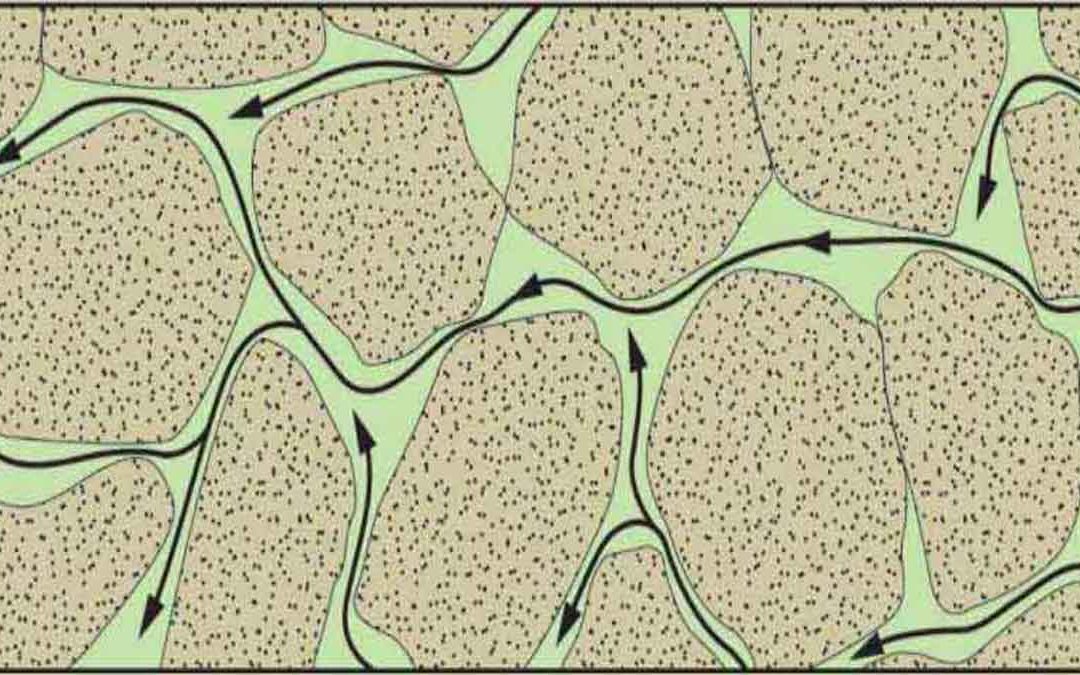
Permeability:
Permeability is the ability of fluids to pass through a process material. It is measured in millidancy (MD) or Darcies (D) and expressed by k.
According to Darcy’s law,
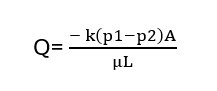
Where,
Q = Rate of fww
K= Permeability
(p1-p2) = Pressure drop across the sample
A = Cross-sectional area of the sample
μ = Viscosity of fluid
L = Length of the sample
The negative sign (-) indicates that fluid moves from a high to a low pressure area.
Classification of Permeability:
Absolute/specific permeability:
When a single fluid phase completely saturates the pore space, then it is referred to as absolute or specific permeability. It is denoted as -K.
Effective permeability:
When the saturation is less than 100%, it affects the effective permeability. At 100% saturation, it ranges between 0 and k, but the sum of permeabilities for two or three phases never exceeds 1. We denote the effective permeability of gas, oil, and water as kg, ko, and kw.
Relative Permeability:
The ratio of the effective permeability for a particular field at a given saturation to a base permeability defines relative permeability. It ranges from 0 to 1. Scientists denote it as kro, kng, and krw for oil, gas, and water, respectively.
Thus,
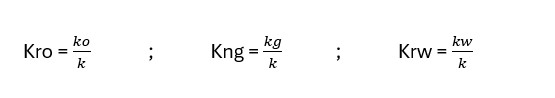
Where, ko,kg,kw = Effective permeability at 100% oil /gas/ water saturation
k = Absolute permeability
Methods of measuring permeability:
Three methods are used to measure permeability.
Drill stem test (DST) / Production text:
This is one of the best ways to measure permeability. In this test, engineers measure the rate of flow and the drop in pressure at the commencement by drilling a well into the reservoir rock. Through this well, they determine all parameters needed to calculate permeability using Darcy’s law. This method allows geologists to determine the productive capacity of geological formations.
Wireline logs:
This procedure is able to identify permeable zones by SP Log & Caliper log.
Permeameter:
This instrument measures permeability. It opens the fastest and can take many readings over a small mock area. It plays a crucial role in analyzing heterogeneous pore systems and heterogeneous rock fabrics. Researchers use various types of permeameters, such as the Probe permeameter and Mini permeameter.