Latest Post & Case Study
Recent Post
Characteristics Of Renewable Natural Resources
Renewable natural resources play a vital role in sustaining life and supporting economic development. Understanding...
Modified Mercalli Scale: Understanding Earthquake Intensity (I–XII)
The Mercalli scale was developed in 1902 and modified in the 1930s. The Mercalli scale assigns a numerical value, from...
Seismology & Its Development
Seismology is the study of earthquakes. Much of the information about the nature of faulting during an earthquake...
Crystallography and Minerals
Physical Characteristics of Minerals
The physical characteristics of minerals are essential traits used to identify and classify them accurately. These...
Classification of Minerals Based on Chemical Composition
The classification of minerals is primarily based on their chemical composition, which allows scientists and...
Types of Clay Minerals
Clay minerals consist of crystalline materials that give soil its plasticity and cohesion. A clayey soil, along with...
Economic & Historical Geology
Seismology & Its Development
Seismology is the study of earthquakes. Much of the information about the nature of faulting during an earthquake...
Major Metallic Minerals in India
Metallic minerals are essential resources for industrial and economic development. Found in various forms across...
James Hutton: Father of Modern Geology
James Hutton, usually described as the "Father of Modern Geology," plays a critical role in the field of Earth...
Petrology
Caused and Types of Joints in Rocks
Joints are natural cracks or fractures in rocks that form when stress exceeds the rock’s strength. Unlike faults, they...
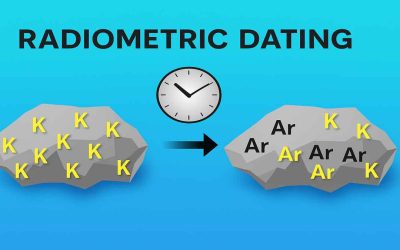
Geological Applications of Radiometric Dating
Radiometric Dating: Introduction and Principles In the early part of the 20th century, scientists discovered...
Evolution of Organic Matter into Petroleum
Petroleum evolves from organic matter through heat, pressure, and time. Initially, buried material transforms into...
Geomorphology
Characteristics Of Renewable Natural Resources
Renewable natural resources play a vital role in sustaining life and supporting economic development. Understanding...
Modified Mercalli Scale: Understanding Earthquake Intensity (I–XII)
The Mercalli scale was developed in 1902 and modified in the 1930s. The Mercalli scale assigns a numerical value, from...
Seismology & Its Development
Seismology is the study of earthquakes. Much of the information about the nature of faulting during an earthquake...