Latest Post & Case Study
Recent Post
Classification of Natural Resources
The classification of natural resources is essential because natural resources vary greatly in their location,...
Density of Soil
The density of soil refers to the mass of soil within a given volume. It helps us understand how compact or loose the...
Tunnel: Components and Types.
A tunnel is a horizontal or slightly inclined underground passage that runs through rock or unconsolidated materials...
Crystallography and Minerals
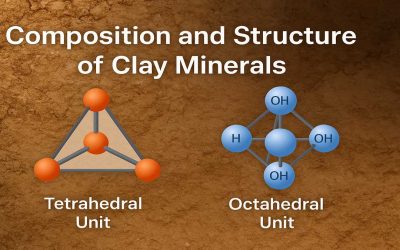
Composition and Structure of Clay Minerals
Clay minerals are microscopic, layered silicate minerals that form the fine fraction of soils and sediments. They...
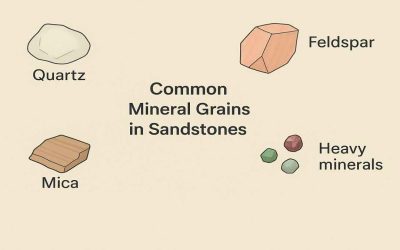
Common Mineral Grains in Sandstones
Mineral Grains in Sandstones: A very large number of different minerals may occur in sandstones, and only the most...
Types of Metamorphic Reactions
Metamorphic Reaction: The study of metamorphic reactions provides vital information about the pressure and temperature...
Economic & Historical Geology
Simple Explanation of Terranes in Geology
What Are Terranes? Terranes are fault-bounded crustal blocks that have distinct lithologic and stratigraphic...
Objectives of Land Use Policy
Land is a valuable resource, and using it wisely is important for sustainable growth. In Bangladesh, the land use...
Sea Level Changes in The Geologic Past
Sea level has never been constant throughout Earth’s history. It has risen and fallen over geological time due to...
Petrology
Natural Gas: Its Origins, Composition and Classification
Natural Gas: Natural gas is a mixture of hydrocarbon (lower) that occurs in nature and exits in a gaseous state at...
Petroleum: Its Physical Properties and Chemical Classification
Petroleum is an essential fossil fuel composed of a natural mixture of hydrocarbons, including crude oil, natural gas,...
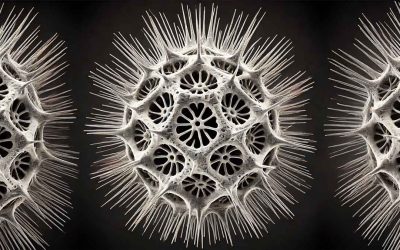
Radiolaria: Its Basis of Classification and Application.
Radiolaria: Radiolaria are free-floating protists with roughly spherical cells and thread-like pseudopodia extending...
Geomorphology
Classification of Natural Resources
The classification of natural resources is essential because natural resources vary greatly in their location,...
Density of Soil
The density of soil refers to the mass of soil within a given volume. It helps us understand how compact or loose the...
Tunnel: Components and Types.
A tunnel is a horizontal or slightly inclined underground passage that runs through rock or unconsolidated materials...