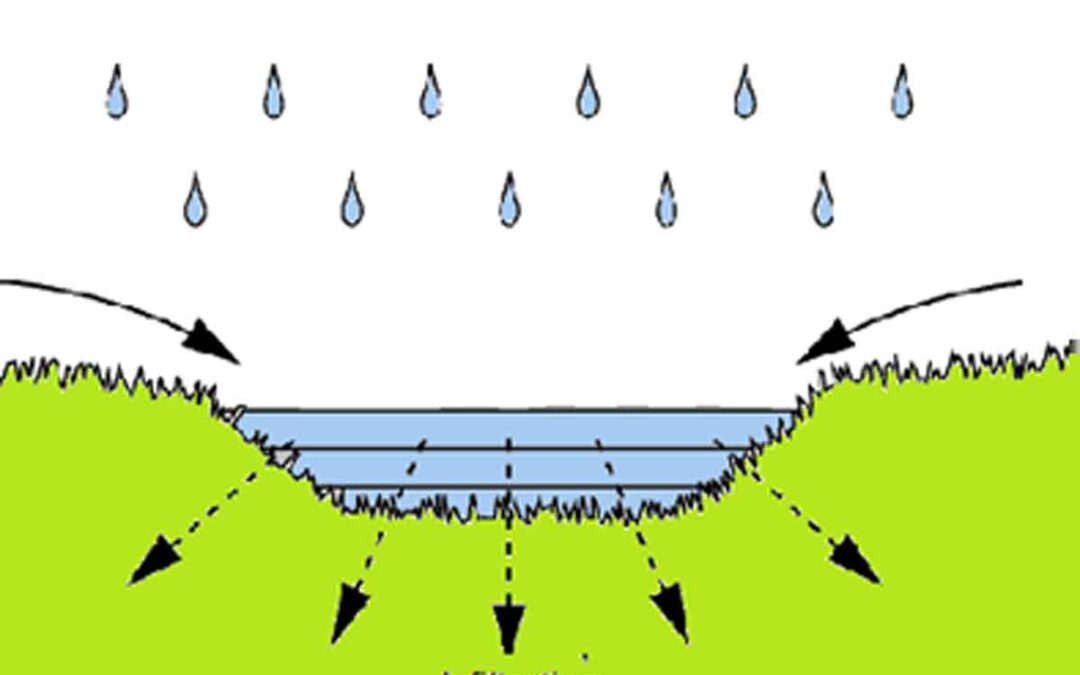
Infiltration is a crucial process in the hydrological cycle. It plays a vital role in maintaining groundwater levels and preventing surface runoff. It has direct implications for agriculture, water management, and environmental sustainability.
Infiltration:
The downward entry of water into the immediate surface of soil or other materials.
Infiltration Capacity:
The maximum rate at which water can infiltrate a soil under a given set of conditions.
Infiltration Rate:
The rate at which water penetrates the soil’s surface and is expressed in cm/hr, mm/hr, or inches/hr. Its rate is limited by the capacity of the soil and the rate at which water is applied to the surface. This is a volume flux of water flowing into the profile per unit of soil surface area (expressed as velocity).
Process:
- It is the process by which water enters the soil from the ground surface
- It first replenishes the soil moisture deficiency
- It is responsible for subsurface and groundwater flow
- The supply to the water reservoir also depends upon infiltration
- The infiltration rate is used for the computation of the water loss due to infiltration for the determination of the surface runoff
Measurement of infiltration:
- Clean the surface vegetation without disturbing the soil surface
- Rings driven into 15 cm
- Put a plastic/polythene sheet to the inner ring and fill water on that for a particular depth
- Water poured into the outer ring and allowed it to infiltrate
- Remove the plastic sheet from the inner ring and start recording depth with time
How to Measure It?
- Double-ring infiltrometer
- Inner = 30cm
- Outer = 50cm
- Measure the inner; maintain a head
- Issues??
- Disc Permeameter and Tension Infiltrometer
- Water held under tension
- Passes through disc at soil surface; measure rate
Importance of Infiltration:
It plays a vital role in ecosystems by performing a variety of important functions.
- Groundwater recharge: Helps recharge groundwater.
- Erosion control: Reduces surface erosion, thereby reducing soil and water loss.
- Agricultural productivity: Maintains soil moisture, which is essential for plant growth.
- Water cycle dynamics: Supports the stability of the water cycle.
Infiltration indices:
An average constant value of infiltration is called the infiltration index. Two types of indices are commonly used.-index
1. φ -index
2. w –index
These are used for the analysis of significant floods when the soil is wet and the rate becomes constant.
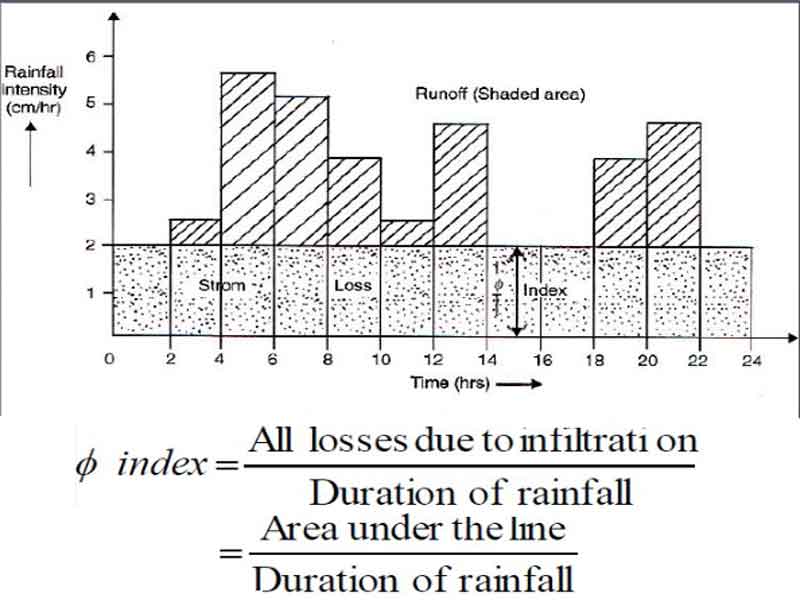
φ -index:
- The value of φ -index can be derived from the rainfall hyetograph and the resulting surface runoff volume by trial and error.
- The unshaded area below the horizontal line is assumed that all losses are due to infiltration only.
- For determination of φ- index, a horizontal line is drawn on the hyetograph such that the shaded area above that line is equal to the volume of surface runoff.
- If the shaded area is not equal to the volume of measured surface runoff, the horizontal line is shifted upwards or downwards till this condition is satisfied.
- Ф-index –average rainfall intensity above which rainfall volume is equal to runoff volume (Ф= Phi)
- The area above the curve is the runoff
- In order to simplify the rate, indices with constant infiltration rates are used
- Its rate is assumed to be constant throughout the rain
w –index:
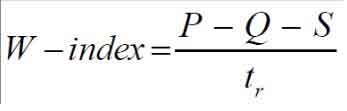
w-index=(P-R-S)/tr
Where,
P = total storm precipitation (cm)
Q = total surface of runoff (cm)
S = depression and interception losses (cm)
Tr = time period (in hours)
Infiltration Rate (Time Dependent):
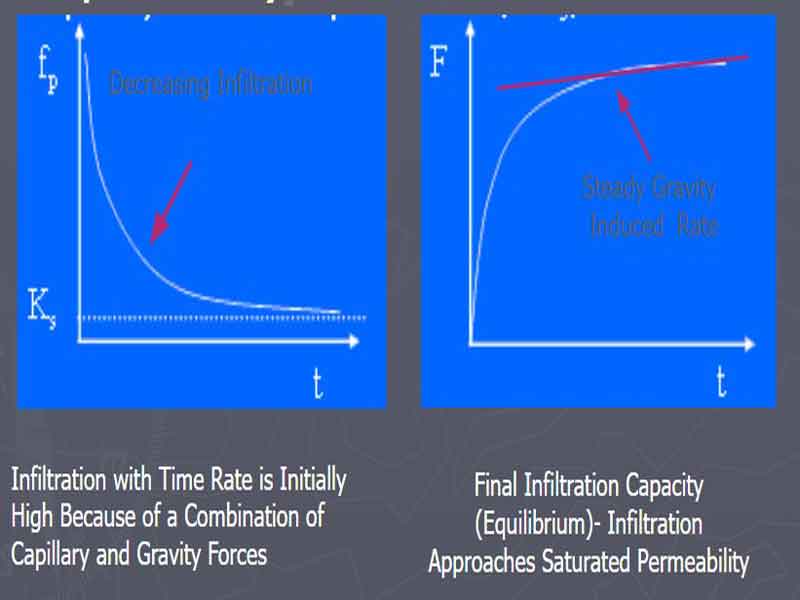
Infiltration Rate (Moisture):
It Decreases with Time
- Changes in Surface and Subsurface Conditions
- Change in Matrix Potential
- Overtime – Matrix Potential Decreases and Gravity Forces, Dominate – Causing a Reduction in the Rate

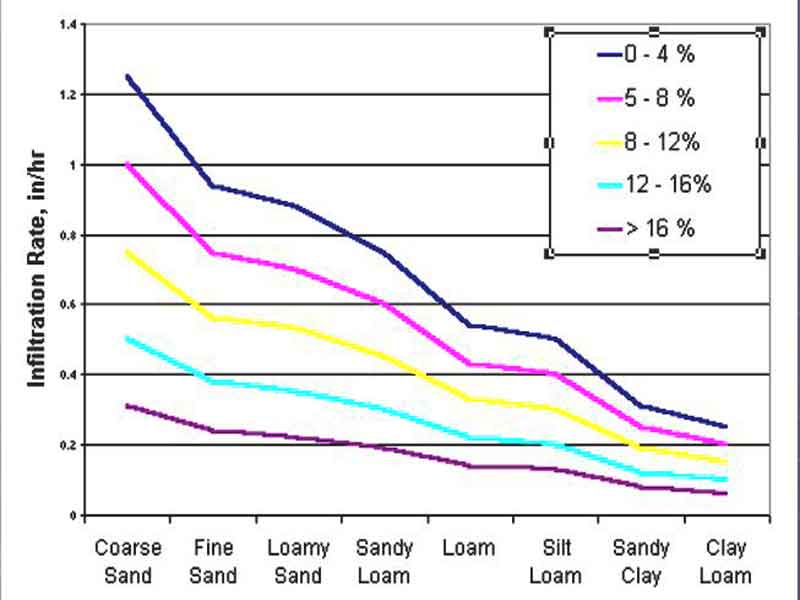
Infiltration Rate Function of Slope & Texture:
Infiltration and Climate Change:
Climate change is changing the way rainwater infiltrates the ground, as well as the amount and intensity of precipitation. Adopting sustainable land and water management practices is key to adapting to these changes and securing water resources.
FAQs:
What is infiltration in simple terms?
It is the process by which water enters the soil from the surface.
How is infiltration measured?
It is measured using tools like infiltrometers or by observing the rate of water absorption into the soil.
Why is important for the water cycle?
It replenishes groundwater, reduces runoff, and maintains the balance of the hydrological cycle.