by Gelogia | Jan 29, 2025 | Mineralogy
Foliated rocks include slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss, and migmatite. Each type varies in grain size, mineral composition, and foliation intensity, reflecting different metamorphic conditions. What are Foliated Rocks? Foliated rock forms when pressure squeezes into...

by Gelogia | Nov 7, 2024 | Mineralogy
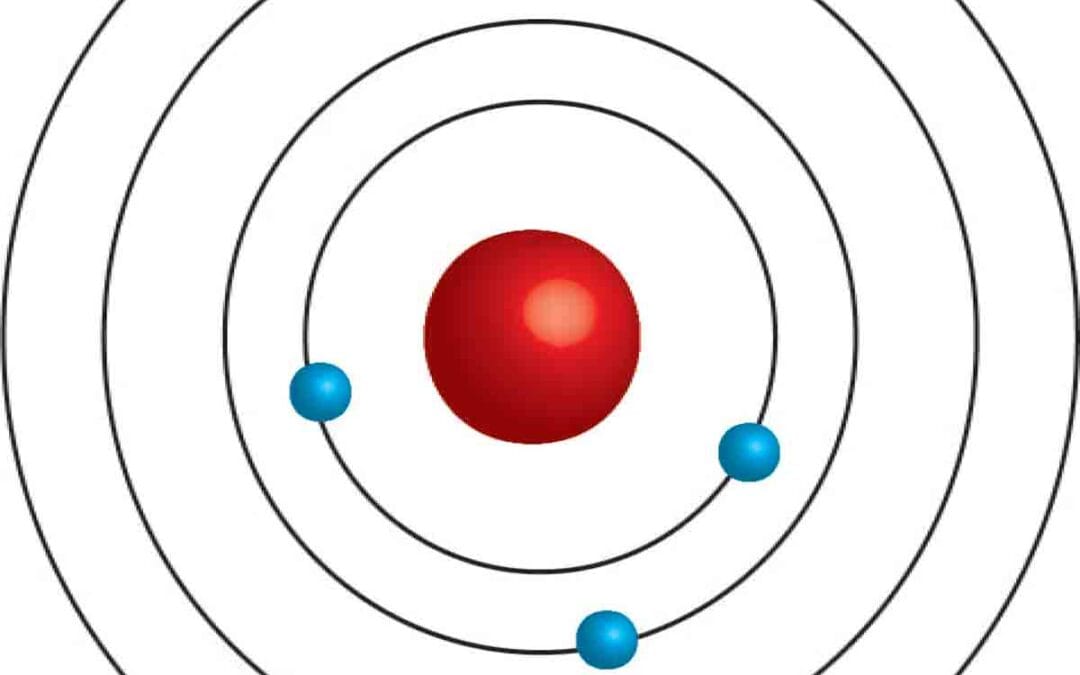
Niels Bohr introduced Bohr’s model of the atom as an enhancement of Rutherford’s atomic model. Rutherford had established a nuclear model that described the atom with a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons. Bohr expanded on this...

by Gelogia | Nov 4, 2024 | Mineralogy
Chemical Equilibrium: When the rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal, the concentration of the reactants and products remains constant. This stage is called chemical equilibrium. Characteristics of Chemical Equilibrium: Constancy of concentration Can...

by Gelogia | Nov 1, 2024 | Mineralogy
Thermodynamics focuses on the interactions between heat, work, and temperature, exploring how these elements connect to energy, entropy, and the physical characteristics of matter and radiation. These interactions are defined by three fundamental laws of...

by Gelogia | Oct 30, 2024 | Mineralogy, Structural Geology
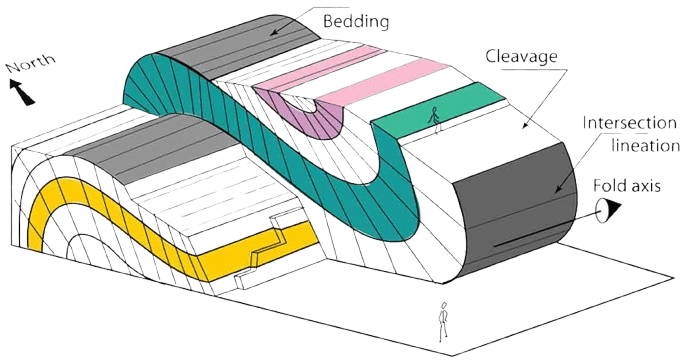
Lineation: Lineation is expressed by the parallelism of some directional property in the rock. Types of lineation: Lineation is found to develop in igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Lineation is of two types: primary lineation (sedimentary rocks, igneous...

by Gelogia | Oct 14, 2024 | Mineralogy
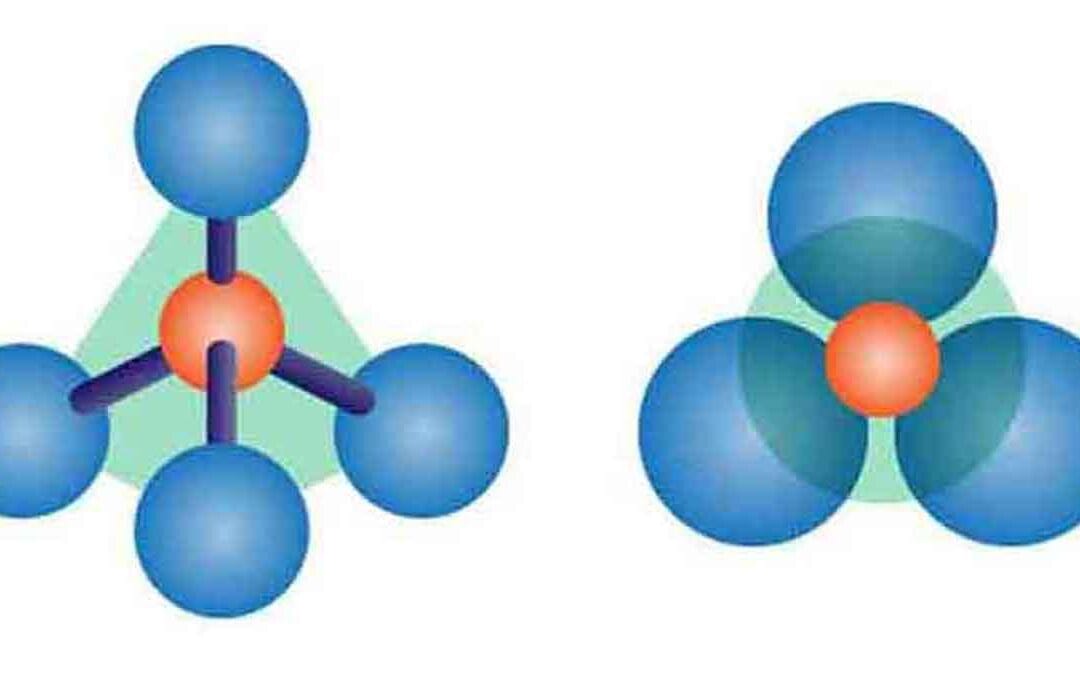
Silicates: Silicates are compounds containing silicon as an anion. The most common silicates are oxides, but hexafluoro silicates and other anions are also included. Silicate minerals contain (SiO4)4- in their structure. Silicates form the largest class of mineral...