Chemical Equilibrium:
When the rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal, the concentration of the reactants and products remains constant. This stage is called chemical equilibrium.
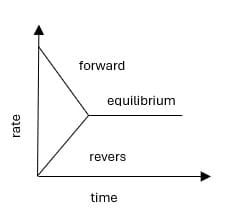
Characteristics of Chemical Equilibrium:
- Constancy of concentration
- Can be initiated from the other side
- Can’t be attained in an open vessel
- A catalyst cannot change the equilibrium point.
- Values of equilibrium constant do not depend upon the initial concentration of reactants
- At equilibrium, ∆G= O
Types of Chemical Equilibrium:
- Homogeneous
- Heterogeneous
Homogeneous :
In this reaction, both the reactants and products involved in chemical equilibrium are present in the same phase.
It can also be categorized into two types:
(1) Reactions where the number of product molecules matches the number of reactant molecules.
For example,
H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2HI(g)
N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2NO(g)
(2) Reactions where the number of product molecules does not match the total number of reactant molecules can occur. For example,
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g)
COCl2(g) ⇌ CO(g) + Cl2(g)
Heterogeneous :
In this kind of reaction, the reactants and the products at chemical equilibrium exist in different phases. For example,
CO2(g) + C(s) ⇌ 2CO(g)
CaCO3(s) ⇌ CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Constant of Chemical Equilibrium:
A certain ratio of reactant and product concentration has a constant value for a reversible reaction at equilibrium and a constant temperature. This is called the equilibrium constant, denoted by ‘K.’
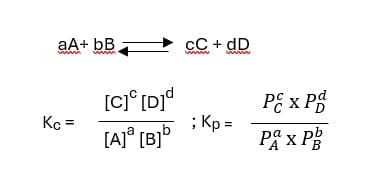
If K >> 1, The equilibrium will lie to the right and favor the product
If K << 1, The equilibrium will lie to the left and reactant the product
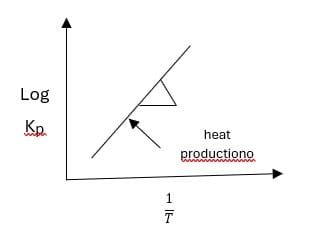
Temperature dependence of equilibrium constant:
Increasing or decreasing in temp causes a change in the equilibrium constant. Vont Hoff’s equation is
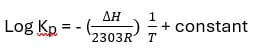
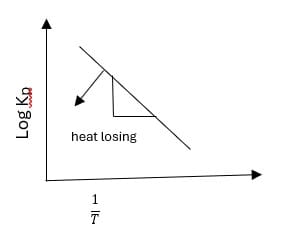
It is similar to a straight-line equation Y = mx + c


Rate of reaction:
The change in concentration of a reactant or a product with time.
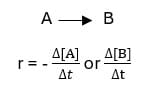
Rate of reaction affected by :
- Concentration of reactants
- Concentration of catalyst
- Temperature
- Surface area of a solid reactant or catalyst






